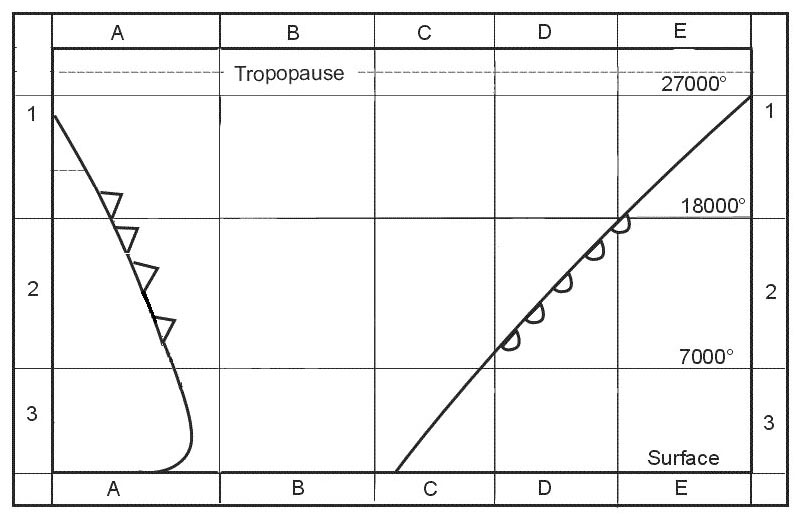
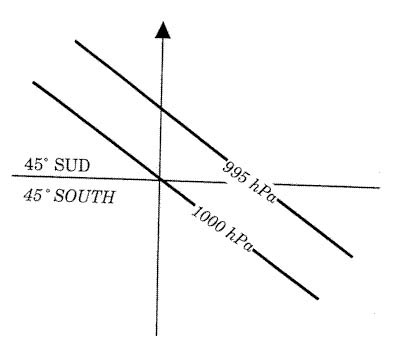
Question 221-1 : Ops regulation.according to easa air ops what is the planning minima for a destination alternate with a cat ii approach available ? [ Certification weather ]
Rvr according to cat i
Question 221-2 : What minimum navigation equipment is required for operations under ifr or under vfr over routes not navigated by reference to visual landmarks ?
One vor receiving system one adf system one dme
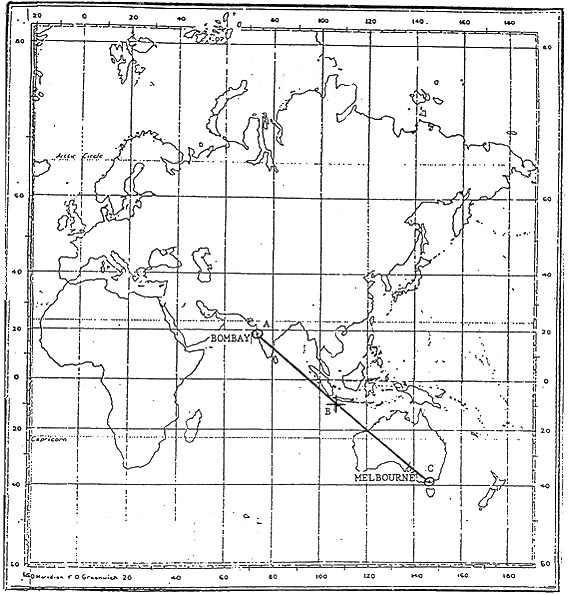
Question 221-3 : A flight via the shannon gander great circle with no mnps certification can be planned ?
Question 221-4 : In the mnps airspace a pilot should first of all take the following action in the event of a failure of the last inertial navigation system ?
Question 221-5 : Easa air ops regulation.according to ops planning minima for a destination aerodrome with an applicable precision approach procedure is ?
Rvr / visibility specified in accordance with air ops part cat
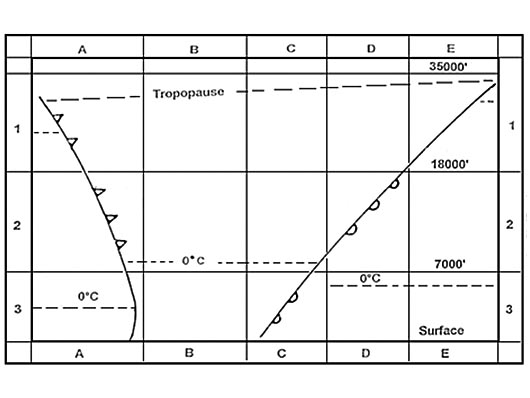
Question 221-6 : Ops regulation.according to air ops what is the planning minima for a destination aerodrome if it is equipped with a non precision approach only ?
Rvr / visibility specified in accordance with air ops and the ceiling at or above mdh
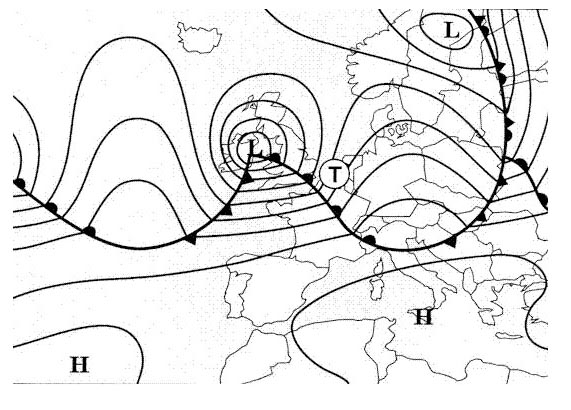
Question 221-7 : What is the planning minima for a destination alternate with a cat i approach available ?
Non precision minima rvr and the ceiling at or above mdh
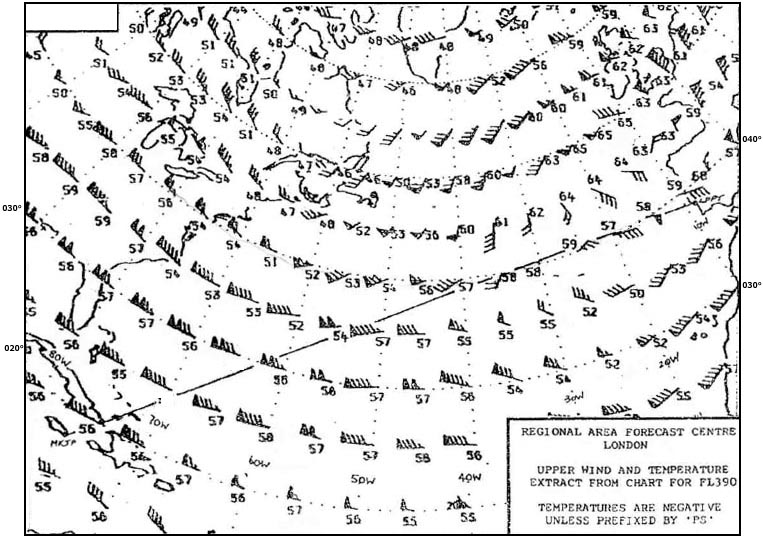
Question 221-8 : The number of hand fire extinguishers which have to be installed in the passenger cabin depends on the approved number of ?
Question 221-9 : In a aeroplane each crew member shall be properly secured by all safety belts and harnesses provided.1 during taxying.2 during take off.3 during landing.4 whenever deemed necessary by the commander in the interest of safety.5 during other phases of the flight while at his station.the combination ?
2 3 4
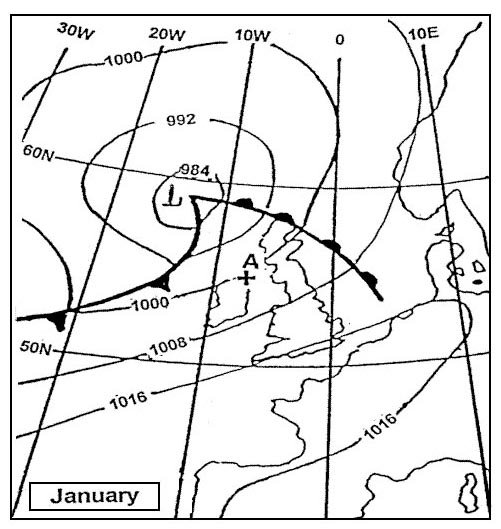
Question 221-10 : Who is responsible for establishing aerodrome operating minima for each aerodrome planned to be used for commercial purposes ?
The operator
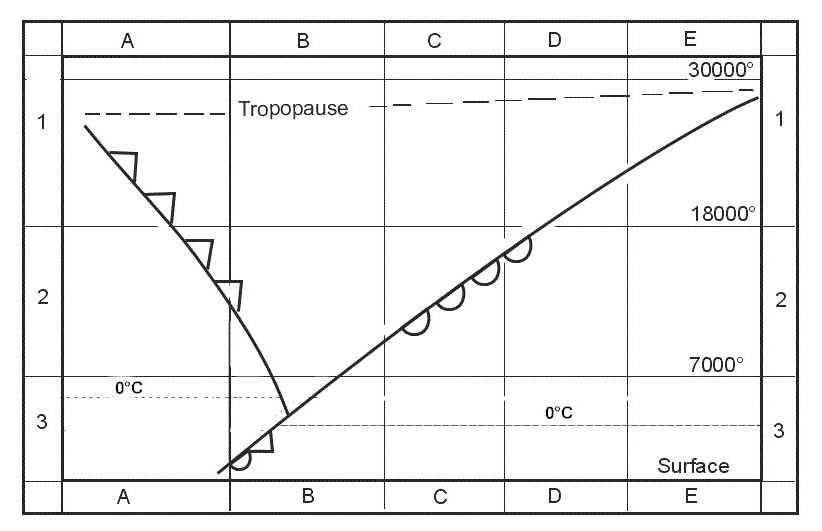
Question 221-11 : Ops regulation.according to air ops the selection of a destination alternate is not required when ?
Question 221-12 : Ops regulation.in accordance with air ops during a vor procedure if the reported rvr/visibility is less than the applicable minima the approach shall not be continued beyond ?
Question 221-13 : Ops regulation.in accordance with air ops where no outer marker or equivalent position exists if the reported rvr/visibility is less than the applicable minima the approach shall not be continued beyond ?
Question 221-14 : Which is the correct statement for pre flight inspections ?
Question 221-15 : Icao annex 6. in accordance with icao annex 6 part i the flight data recorder is to be located in the aircraft ?
Question 221-16 : An aerodrome with weather reports indicating that the weather conditions are at or above operation minima from one hour prior to one hour after the anticipated arrival is defined as ?
Question 221-18 : The set processes by which an aircraft with the applicable airworthiness requirements and remains in a condition for safe operation is called as ?
Continuing airworthiness
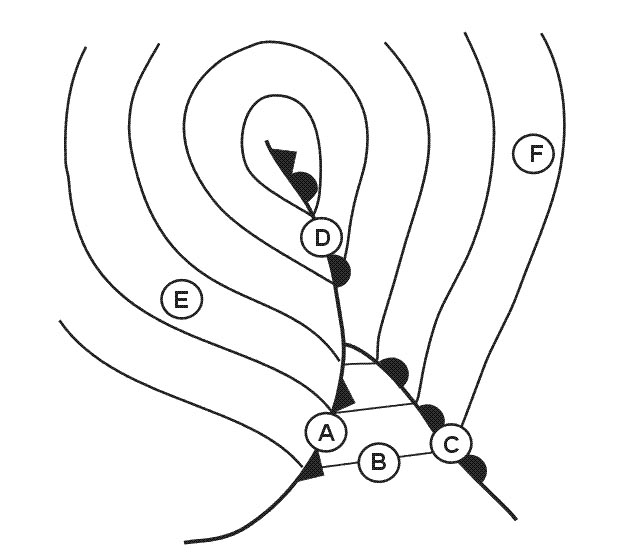
Question 221-19 : An operator shall ensure that employees when abroad know that they must comply with the laws regulation and procedures of ?
Question 221-20 : An authorized operator to conduct international commercial air transport operation shall be comply with ?
Question 221-21 : Flight and duty time limitations and rest requirements.the maximum daily flight duty period fdp can be extended up to ?
1 hour
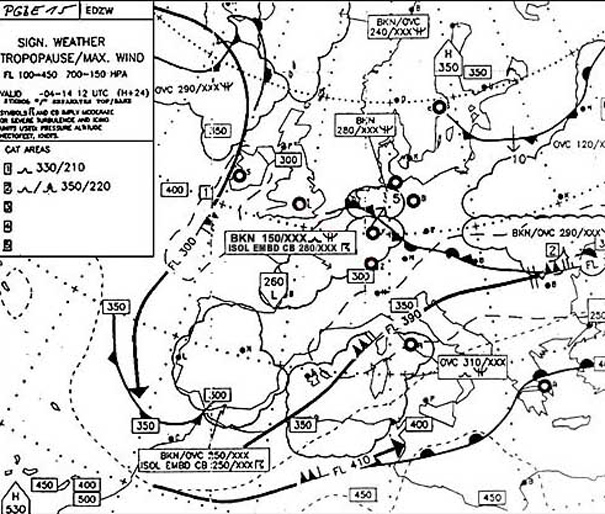
Question 221-22 : Flight and duty time limitations and rest requirements.window of circadian low wocl is the time between ?
Question 221-23 : Flight and duty time limitations and rest requirements.the 'local night' means a period of 8 hours falling between ?
Question 221-24 : Flight and duty time limitations and rest requirements.'standby' is a period of time included in ?
Duty period
Question 221-25 : Flight and duty time limitations and rest requirements.the time spent at the airport between two flights is part of the ?
Duty period
Question 221-26 : Flight and duty time limitations and rest requirements.according to easa oro ftl flight and duty time limitations and rest requirements 'night duty' means ?
A duty period encroaching any portion of the period between 02 00 and 04 59 in the time zone to which the crew is acclimatised
Question 221-27 : Flight and duty time limitations and rest requirements.the total duty periods to which a crew member may be assigned shall not exceed ?
60 duty hours in any 7 consecutive days
Question 221-28 : Instruments and equipment.it is recommended that first aid kits should be positioned ?
Near exits
Question 221-29 : A flight may be conducted under vfr only if ?
Question 221-31 : Annex 6.'flight time' definition ?
The total time from the moment an aeroplane first moves for the purpose of taking off until the moment it finally comes to rest at the end of the flight
Question 221-32 : With regard to the management system an operator is required to establish implement and maintain such system shall correspond to the .1 complexity of operation and size of the company.2 annual income level of the company.3 annual profit/loss and the number of passengers carried.4 complexity of ?
1 4
Question 221-33 : Which of the following is the correct definition of 'dry lease' ?
The aircraft is operated under the aoc of the person to whom it is leased
Question 221-34 : Seats should be allocated for ?
Question 221-35 : Who is responsible for ensuring cabin crew members are qualified in their duties ?
The operator
Question 221-36 : In accordance with easa air ops the operator must ensure that the dangerous goods documentation of a flight is stored for a minimum period of ?
3 months
Question 221-37 : Ops regulation.in accordance with air ops the commander of an aeroplane with reciprocating engines should have a final reserve fuel for ?
Question 221-38 : In accordance with the easa air ops an airplane with one passenger deck equipped with 245 passenger seats and effectively carrying 195 passengers is scheduled to fly 8 hour flight from paris to new york 90 minute etops route it must be equipped with ?
1 emergency medical kits
Question 221-39 : The commander shall declare an emergency when the ?
Calculated usable fuel on landing at the nearest adequate aerodrome where a safe landing can be performed is less than final reserve fuel
Question 221-40 : What is the reason for selecting a suitable take off alternate aerodrome ?
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
8799 Free Training Exam