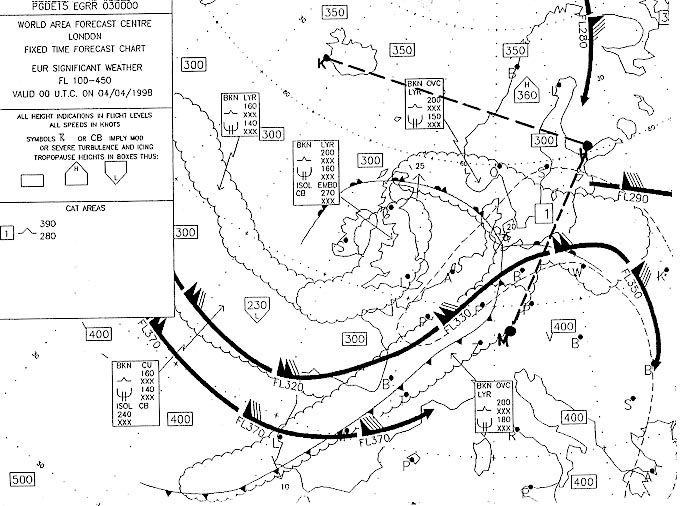
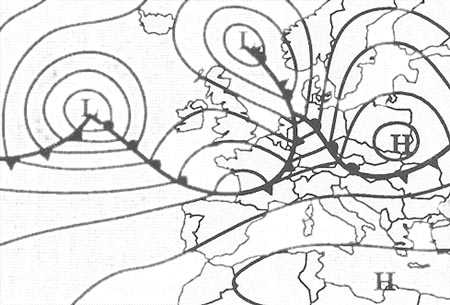
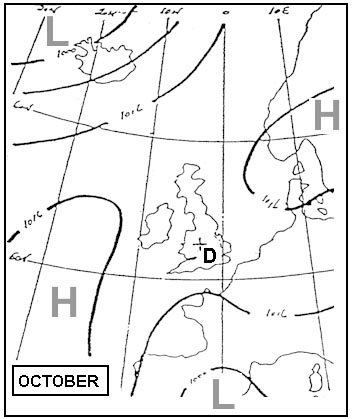
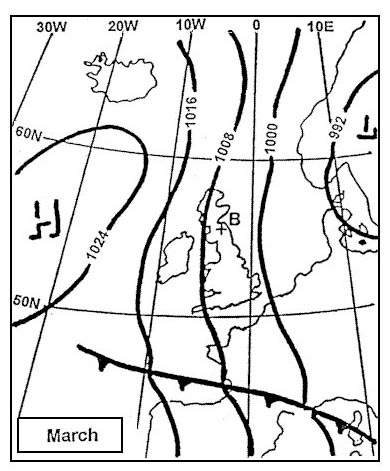
Question 71-1 : The database of a fms flight management system is divided into major sections ? [ Practice protocol ]
Question 71-2 : For most fms the fuel prediction function which computes the remaining fuel among the flight plan takes into account the following parameters .1 the additional drag in case the landing gear can not be retracted.2 the cruise flight level.3 the additional drag in case the flaps are blocked and ?
Question 71-3 : Under normal conditions in a dual fms architecture the master fmc sends its commands to the .fmc=flight management computer ?
Question 71-4 : The purpose of the flight management system fms is to provide ?
Question 71-5 : A fms can correct its fuel computations for the following non standard configurations .1 landing gear down.2 speed brakes extended.3 one engine out.4 slats/flaps not fully retracted.the combination which regroups all of the correct statements is ?
Question 71-6 : The fms 'autotune' function can automatically tune frequencies for ?
Question 71-7 : In order to enter a phantom waypoint that is designated by a vor/dme simple rnav system the vor/dme ?
Does not have to be in range when entered but must be when used
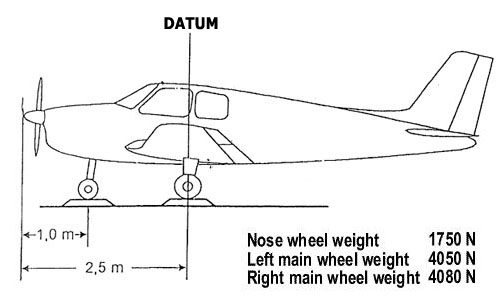
Question 71-8 : Which of the following combinations is likely to result in the most accurate area navigation rnav fixes ?
Dme/dme
Question 71-9 : Which of the following gives the best information about the progress of a flight between 2 en route waypoints from a 'rnav' equipment ?
Question 71-10 : If an aircraft flies along a vor radial it will follow a ?
Great circle track
Question 71-11 : Which of the figures depicts an electronic flight instrument system efis display in expanded exp vor/ils mode with an ils frequency selected . 2067 ?
Question 71-12 : Which of the figures depicts an electronic flight instrument system efis display in expanded exp vor/ils mode with a vor frequency selected . 2103 ?
Question 71-13 : Which of the figures depicts an electronic flight instrument system efis display in full vor/ils mode with an vor frequency selected . 2102 ?
Question 71-14 : Which of the figures depicts an electronic flight instrument system efis display in plan mode . 2100 ?
Question 71-15 : Which of the figures depicts an electronic flight instrument system efis display in map mode . 2100 ?
Question 71-16 : Which of the figures depicts an electronic flight instrument system efis display in expanded exp vor/ils mode with an vor frequency selected . 2100 ?
Question 71-17 : Which of the figures depicts an electronic flight instrument system efis display in expanded exp vor/ils mode with an ils frequency selected . 2100 ?
Question 71-18 : Which of the figures depicts an electronic flight instrument system efis display in full vor/ils mode with an ils frequency selected . 2100 ?
Question 71-19 : What drift is being experienced . 2096 ?
8° left
Question 71-20 : What is the value of the track from tbx to ytb . 2094 ?
Question 71-24 : The letters qtx and adjacent symbol indicate a . 2091 ?
Question 71-25 : The 'o' followed by the letters kabc indicate . 2090 ?
Question 71-27 : The diagram indicates that the aircraft is to the . 2087 ?
Question 71-28 : In which screen modes of an electronic horizontal situation indicator ehsi will radar returns not be shown ?
Question 71-29 : Icao annex 11 defines area navigation rnav as a method of navigation which permits aircraft operation on any desired flight path ?
Within the coverage of station referenced navigation aids or within the limits of the capability of self contained aids or a combination of these
Question 71-30 : Basic rnav requires a track keeping accuracy of ?
+/ 5nm or better for 95% of the flight time
Question 71-31 : The flight management computer fmc position is ?
Question 71-32 : Under easa cs 25 color code rules features displayed in red on an electronic flight instrument system efis indicate ?
Question 71-33 : Under easa cs 25 colour code rules features displayed in amber/yellow on an electronic flight instrument system efis indicate ?
Question 71-34 : Under easa/cs 25 colour code rules features displayed in green on an efis should indicate ?
Question 71-35 : Under easa cs 25 colour code rules features displayed in cyan/blue on an electronic flight instrument systems efis indicate ?
Question 71-36 : In an electronic flight instrument system efis data relating primarily to navigation in the fmc is provided by ?
Question 71-37 : Under easa regulations color code rules for efis displays the recommended color for the aircraft symbol is ?
Question 71-38 : Which of the following procedures must be adopted if on a flight under ifr conditions using a navstar/gps satellite navigation system receiver the position fix obtained from the gps receiver differs from the position of conventional navigation systems by an unacceptable amount ?
Question 71-39 : What datum is used for the minimum descent altitude mda on a non precision approach when using the navstar/gps satellite navigation system ?
Barometric altitude
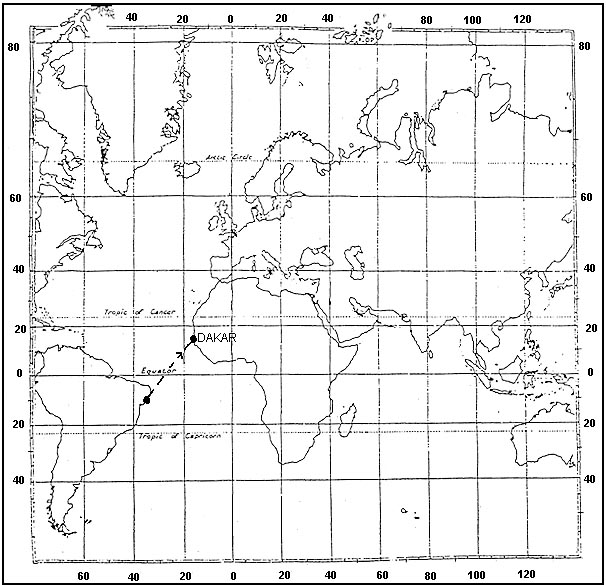
Question 71-40 : Which of the distances indicated will be shown on a basic vor/dme based area navigation equipment when using a 'phantom station' at position 'x' . 2088 ?
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2799 Free Training Exam