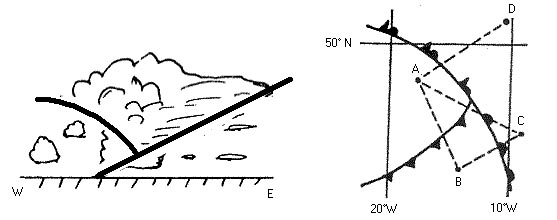
Question 14-1 : Guidance material related to simultaneous operations on parallel or near parallel instrument runways may be found… ? [ Analysis topography ]
In an icao document

Question 14-2 : Regulation eu no 965/2012 as amended lays down detailed rules on certain aspects of aviation safety which of the following are covered by that regulation ?
Commercial air transport operations with aeroplanes and helicopters
Question 14-3 : Two aircraft are flying towards a vor to hold the lowest level of the hold is fl140 aircraft a arrives first and is assigned fl160 aircraft b arrives after what level should aircraft b be assigned in the hold ?
Fl170
Question 14-4 : What should be done if an ra is triggered in the cockpit ?
Manoeuvre to the minimum extent necessary to comply with the ra
Question 14-5 : To which categories of aircraft is regulation 965/2012 applicable ?
Motor powered and non motor powered aircraft involved in commercial air transport operations cat and complex and other than complex motor powered aircraft involved in non commercial operations
Question 14-6 : Which of the following lists all the subparts of annex v to the eu regulation no 965/2012 easa air ops part spa ?
General requirements performance based navigation pbn operations operations with specified minimum navigation performance mnps operations in airspace with reduced vertical separation minima rvsm low visibility operations lvo extended range operations with two engine aeroplanes etops transport of dangerous goods helicopter operations with night vision imaging systems helicopter hoist operations helicopter emergency medical service operations helicopter offshore operations
Question 14-7 : Which of the following lists all subparts of annex vi to the eu regulation no 965/2012 easa air ops part ncc ?
General requirements operational procedures aircraft performance and operating limitations instruments data and equipment
Question 14-8 : An ils approach is being flown given och 167 ft . operational margin 33 ftwhat is the correct approach minimum ?
Dh is 200 ft
Question 14-9 : Complete the following phrase . is a defined area symmetrically disposed about the nominal flight track in which full obstacle clearance is provided ?
Primary area
Question 14-10 : The och is 150 ft for a visual circling approach into an aerodrome given the following heights aerodrome elevation 35 ft . rwy 01 threshold elevation 39 ft . rwy 19 threshold elevation 30 ftwhat is the oca for rwy 01 ?
185 ft
Question 14-11 : What must a pilot do if an ra is triggered in the cockpit ?
Respond by following the ra and inform atc because atc doesn't have communication with acas
Question 14-12 : Where the transition altitude is shared between 2 different aerodromes the common transition altitude shall be… ?
The highest between 2 aerodromes
Question 14-13 : A control zone shall extend laterally to at least ?
5 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned in the direction from which approaches may be made
Question 14-14 : A controlled airspace extending upwards from a specified limit above the earth is ?
Control area
Question 14-15 : A controlled airspace extending upwards from the surface of the earth to a specified upper limit is ?
Control zone
Question 14-16 : Which is the content of section 2 of air report airep ?
Question 14-17 : A lower limit of a control area shall be established at a height above the ground level or water of not less than ?
200 metres
Question 14-18 : A minimum vertical separation shall be provided until aircraft are established inbound on the ils localizer course and/or mls final approach track this minimum is when independent parallel approaches are being conducted ?
300 m 1000 ft
Question 14-19 : A 'rnav' distance based separation minimum may be used at the time the level is crossed provided that each aircraft reports its distance to or from the same 'on track' way point this minimum is ?
80 nm
Question 14-20 : A separation minimum shall be applied between a light or medium aircraft and a heavy aircraft and between a light aircraft and a medium aircraft when the heavier aircraft is making a low or missed approach and the lighter aircraft is landing on the same runway in the opposite direction or on a ?
Less than 760 m
Question 14-21 : A so called 'visual approach' can be performed ?
During ifr flights if there is permanent sight on the movement area and the underlying ground
Question 14-22 : A special air report comprises a number of sections in section i the pilot fills in ?
A position report including aircraft identification height position and time
Question 14-23 : A strayed aircraft is ?
Question 14-24 : A vfr flight when flying inside an ats airspace classified as b has to maintain the following minima of flight visibility and distance from clouds ?
5 km below 3050 m 10 000 ft ams 1 500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds
Question 14-25 : A vfr flight when flying inside an ats airspace classified as c has to maintain the following minima of flight visibility and distance from clouds ?
8 km at or above 3050 m 10000 ft amsl 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds
Question 14-26 : According to international agreements wind direction shall be adjusted to the local variation and given in degrees magnetic ?
Question 14-27 : Aerodrome control service priority for landing .if an aircraft enters the traffic circuit without proper authorisation ?
It shall be permitted to land if its actions indicate that it so desires
Question 14-28 : Air traffic control service is provided for the purpose of ?
Preventing collisions between aircraft between aircraft and obstacles on the manoeuvring area and expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of air traffic
Question 14-29 : Air traffic service unit means ?
Air traffic control units flight information centres or air services reporting offices
Question 14-30 : Air traffic services unit clocks and other time recording devices shall be checked as necessary to ensure correct time to within plus or minus ?
30 seconds of utc at all times
Question 14-31 : Aircraft flying along the same track may be separated by dme distances from the same dme and it is confirmed that the aircraft have passed each other specify the shortest difference in dme distance to make it possible for one aircraft to climb or descend ?
10 nm
Question 14-32 : Airspace classification services.during a 'visual approach' in controlled airspace class c ?
Atc will provide separation with other traffic
Question 14-33 : Altimeter setting change during climb .on flights in accordance with ifr the change of the altimeter setting from qnh to standard shall be made at the ?
Transition altitude
Question 14-34 : The transition level ?
Question 14-35 : Altimeter setting procedures transition altitude .the transition altitude of an aerodrome shall be as low as possible but normally not less than ?
3000 ft
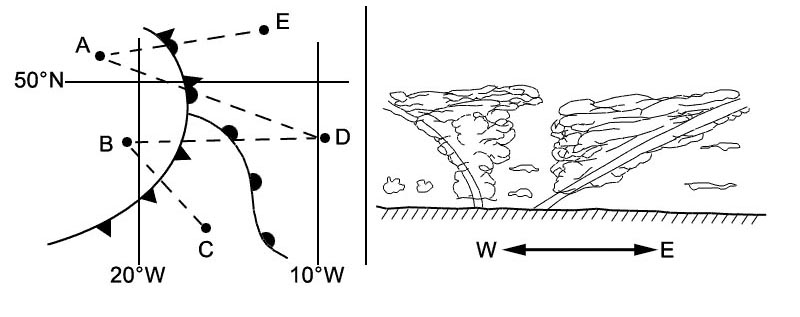
Question 14-36 : Altimeter setting procedures transition layer .unless instructed otherwise by an air traffic controller when passing through the transition layer a pilot shall report the vertical position of the aircraft as ?
Altitude in a descent
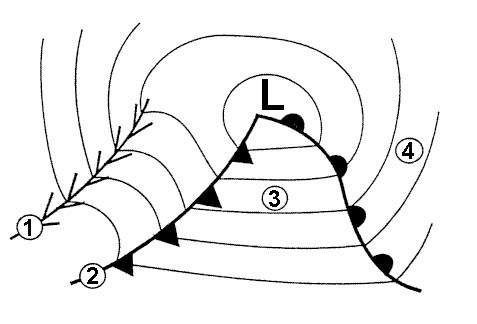
Question 14-37 : Altimeter setting procedures transition level .the vertical position of an aircraft at or above the transition level with altimeter setting 1013 2 hpa has to be reported ?
Question 14-39 : An air traffic control unit ?
Question 14-40 : An aircraft in climb or descent is considered to have crossed a level when the ssr mode c derived level information indicates that it has passed this level in the required direction by ?
More than 300 ft
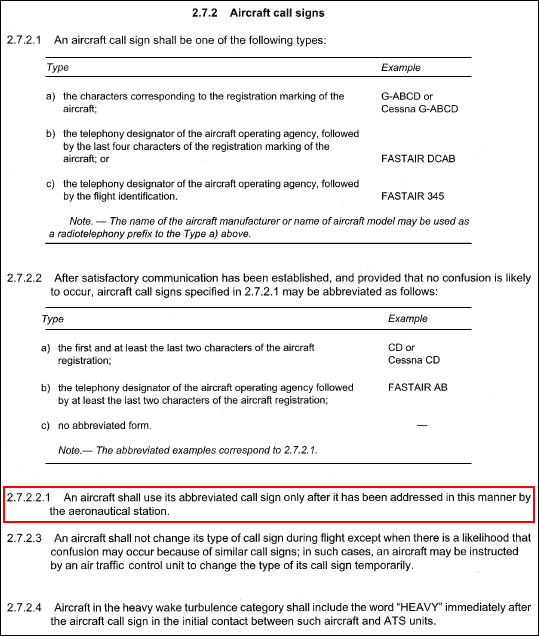
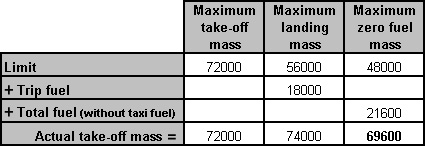
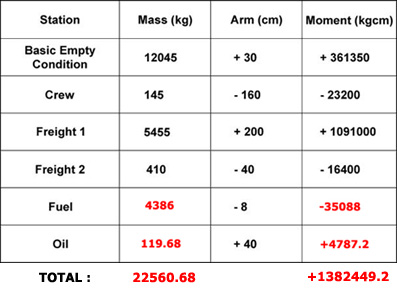
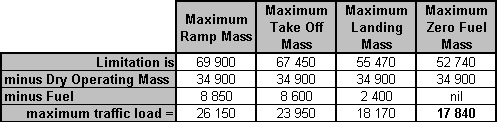
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
519 Free Training Exam Other source study: Afis exam examen 14