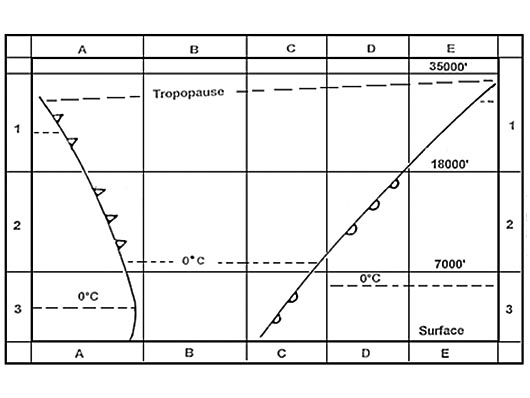
Question 232-1 : The high lift device shown in the figure below is a . err a 081 182 ? [ Formation assignment ]
Question 232-3 : The frontal area of a body placed in a certain airstream is increased by a factor 3 the shape will not alter the aerodynamic drag will increase with a factor ?
Question 232-4 : The aerodynamic drag of a body placed in a certain airstream depends amongst others on ?
Question 232-5 : A body is placed in a certain airstream the airstream velocity increases by a factor 4 the aerodynamic drag will increase with a factor ?
Question 232-6 : A body is placed in a certain airstream the density of the airstream decreases to half of the original value the aerodynamic drag will decrease with a factor ?
Question 232-7 : The point where the aerodynamic lift acts on a wing is ?
The centre of pressure
Question 232-8 : The location of the centre of pressure of a positively cambered aerofoil section at increasing angle of attack will ?
Shift forward
Question 232-11 : A laminar boundary layer is a layer in which ?
No velocity components exist normal to the surface
Question 232-12 : The subsonic static pressure ?
Question 232-13 : The lift and drag forces acting on a wing cross section ?
Depend on the pressure distribution about the wing cross section
Question 232-14 : The lift force acting on an aerofoil no flow separation ?
Question 232-16 : The aerofoil polar is ?
A graph of the relation between the lift coefficient and the drag coefficient
Question 232-17 : Aspect ratio of a wing is the ratio between ?
Wing span squared and wing area
Question 232-18 : Dihedral of the wing is ?
The angle between the 0 25 chord line of the wing and the lateral axis
Question 232-20 : Flap extension at constant ias whilst maintaining straight and level flight will increase the ?
Question 232-21 : When trailing edge flaps are extended whilst maintaining straight and level flight at constant ias ?
Question 232-22 : Which of the following situations leads to a decreasing stall speed ias ?
Question 232-23 : The difference between ias and tas will ?
Decrease with decreasing altitude
Question 232-24 : Compared with stalling airspeed vs in a given configuration the airspeed at which stick shaker will be triggered is ?
Greater than vs
Question 232-25 : The term angle of attack in a two dimensional flow is defined as ?
Question 232-26 : The critical angle of attack ?
Remains unchanged regardless of gross weight
Question 232-27 : Comparing the lift coefficient and drag coefficient at normal angle of attack ?
Cl is much greater than cd
Question 232-28 : Which statement is correct regarding cl coefficient of lift and the angle of attack ?
For a symmetrical aerofoil section if the alpha is zero cl is zero
Question 232-29 : The mean aerodynamic chord mac for a given wing of any planform is ?
The chord of a rectangular wing with same moment and lift
Question 232-30 : Induced drag may be reduced by ?
An increase in aspect ratio
Question 232-31 : The relationship between induced drag and the aspect ratio is ?
A decrease in the aspect ratio increases the induced drag
Question 232-32 : A high aspect ratio wing produces ?
A decrease in induced drag
Question 232-33 : What will happen in ground effect ?
Question 232-34 : Which statement is correct about the laminar and turbulent boundary layer ?
Question 232-35 : Behind the transition point in a boundary layer ?
The mean speed and friction drag increases
Question 232-36 : When trailing edge flaps are extended in level flight the change in pitching moment ignoring any effects on the tailplane will be ?
Question 232-39 : What factors determine the distance travelled over the ground of an aeroplane in a glide ?
The wind and the lift/drag ratio which changes with angle of attack
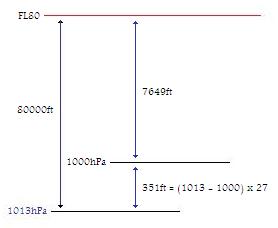
Question 232-40 : The following unit of measurement kgm/s² is expressed in the si system as ?
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
9239 Free Training Exam