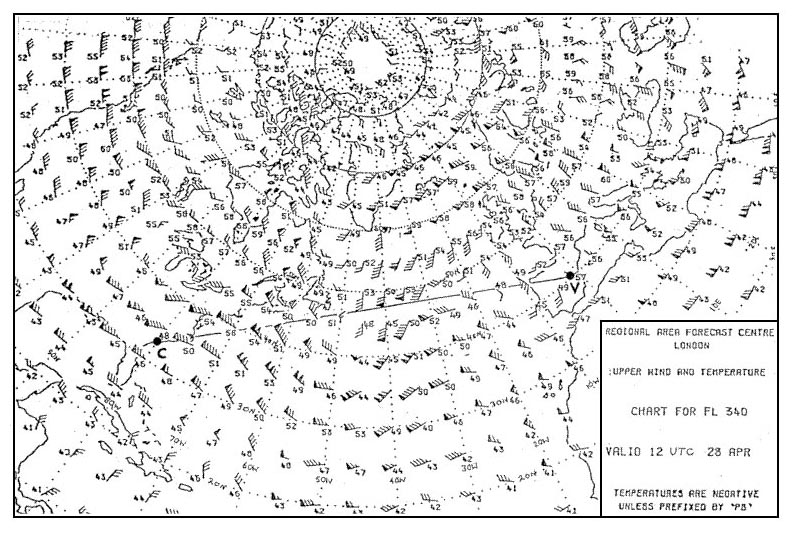
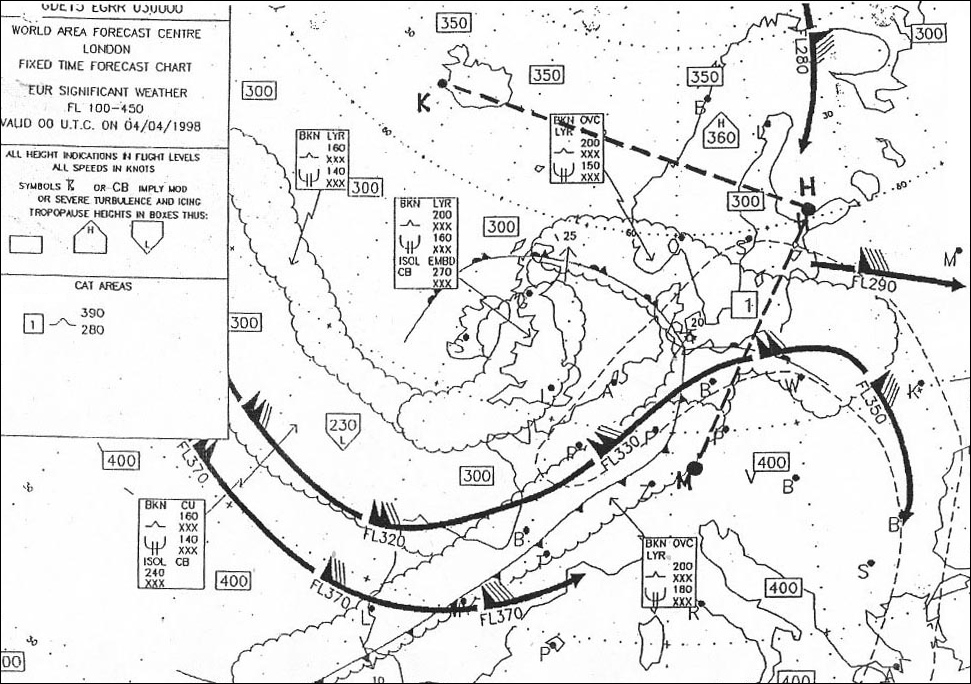
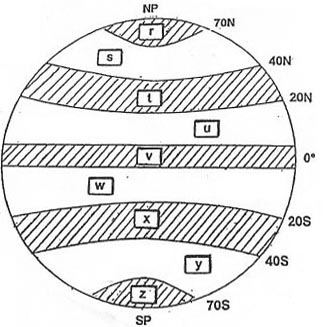
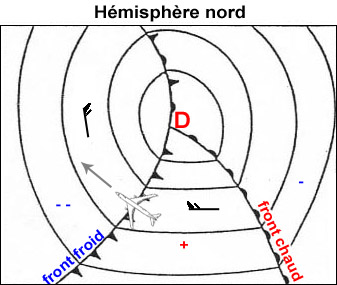
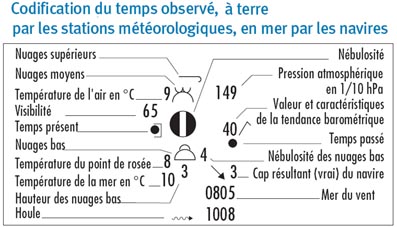
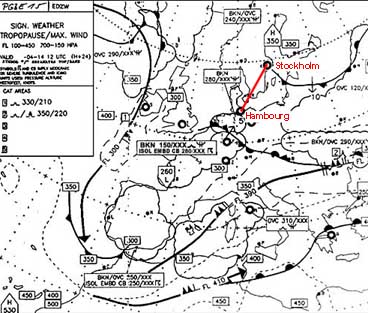
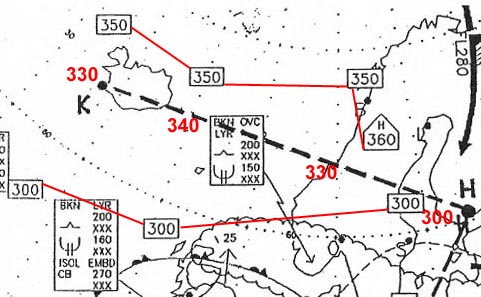
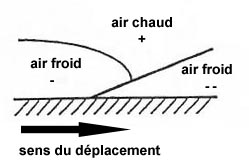
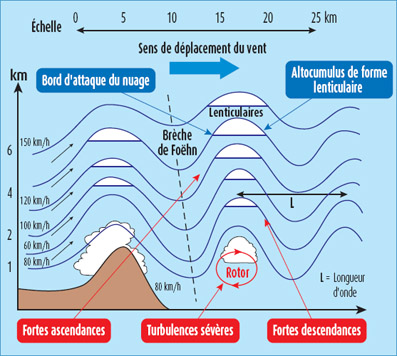
Question 238-1 : The diagram shows the parameter x versus tas if a horizontal flight is considered the axis x shows . err a 081 1319 ? [ Formation assignment ]
The coefficient of lift
Question 238-2 : The additional increase in drag at mach numbers above the critical mach number is due to ?
Question 238-3 : Air passes a normal shock wave which of the following statements is correct ?
Question 238-4 : The bow wave will first appear at ?
Question 238-5 : Two methods to increase the critical mach number are ?
Thin aerofoils and sweepback of the wing
Question 238-6 : A commercial jet aeroplane is performing a straight descent at a constant mach number with constant mass the operational speed limit that may be exceeded is ?
Vmo
Question 238-7 : 'tuck under' is the ?
Question 238-8 : 'tuck under' may happen at ?
Question 238-9 : Which of these statements about 'tuck under' are correct or incorrect . i 'tuck under' is caused by an aft movement of the centre of pressure of the wing . ii 'tuck under' is caused by a reduction in the downwash angle at the location of the horizontal stabiliser ?
I is correct ii is correct
Question 238-10 : An a 310 aeroplane weighing 100 tons is turning at fl 350 at constant altitude with a bank of 50 degrees its flight mach range between low speed buffeting and high speed buffeting goes from . err a 081 100 ?
Question 238-11 : With increasing altitude and constant ias the static lateral stability 1 and the dynamic lateral/directional stability 2 of an aeroplane with swept back wing will ?
1 increase 2 decrease
Question 238-12 : A jet transport aeroplane is in a straight climb at a constant ias and constant weight the operational limit that may be exceeded is ?
Mmo
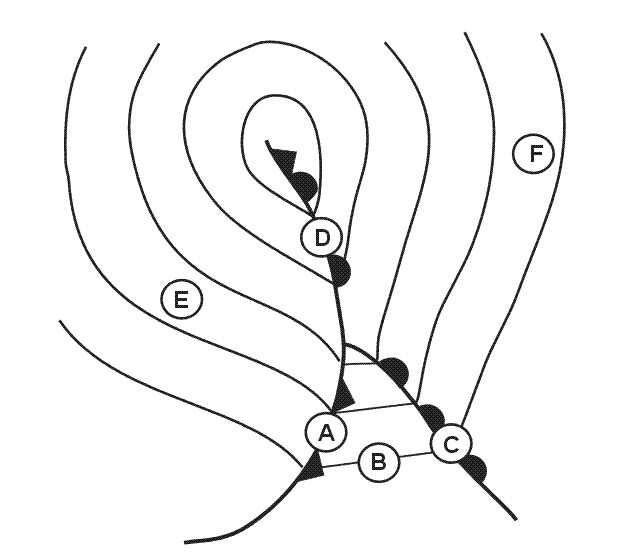
Question 238-13 : What data may be obtained from the buffet onset boundary chart ?
Question 238-14 : Mcrit is the free stream mach number at which ?
Question 238-15 : Which of the following 1 aerofoils and 2 angles of attack will produce the lowest mcrit values ?
1 thick and 2 large
Question 238-16 : The consequences of exceeding mcrit in a swept wing aeroplane may be assume no corrective devices straight and level flight ?
Buffeting of the aeroplane and a tendency to pitch down
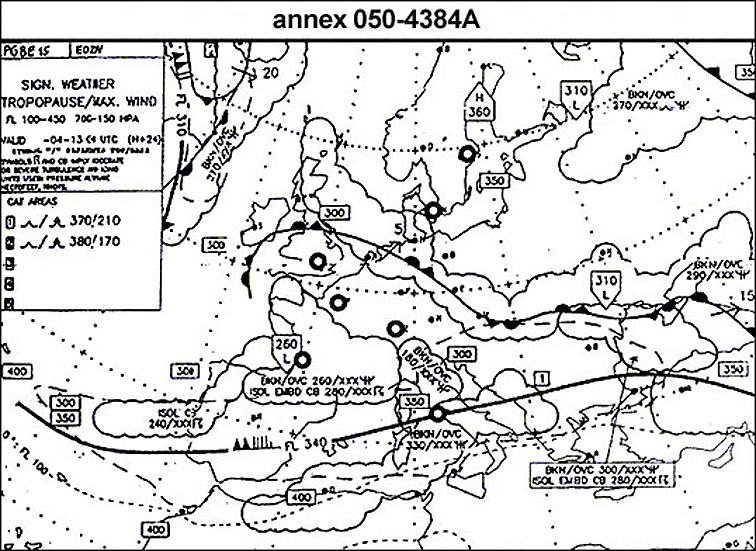
Question 238-17 : A jet aeroplane cruises buffet free at constant high altitude which type of stall is most likely to occur if this aeroplane decelerates during an inadvertent increase in load factor ?
Accelerated stall
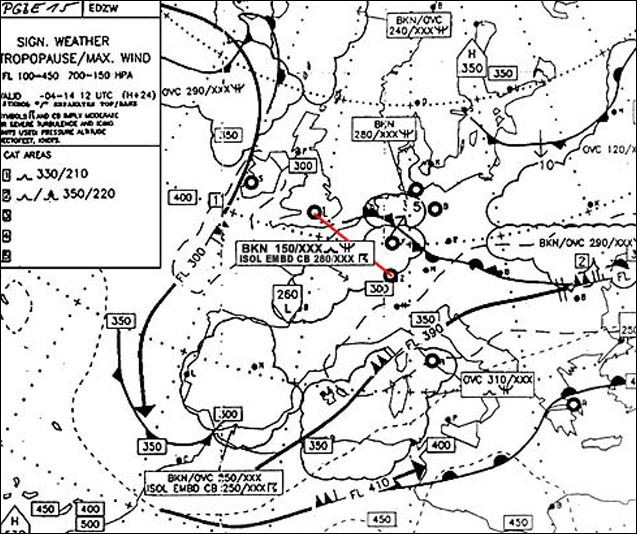
Question 238-18 : As the mach number increases from subsonic to supersonic the centre of pressure moves ?
Question 238-19 : The aft movement of the centre of pressure during the acceleration through the transonic flight regime will ?
Increase the static longitudinal stability
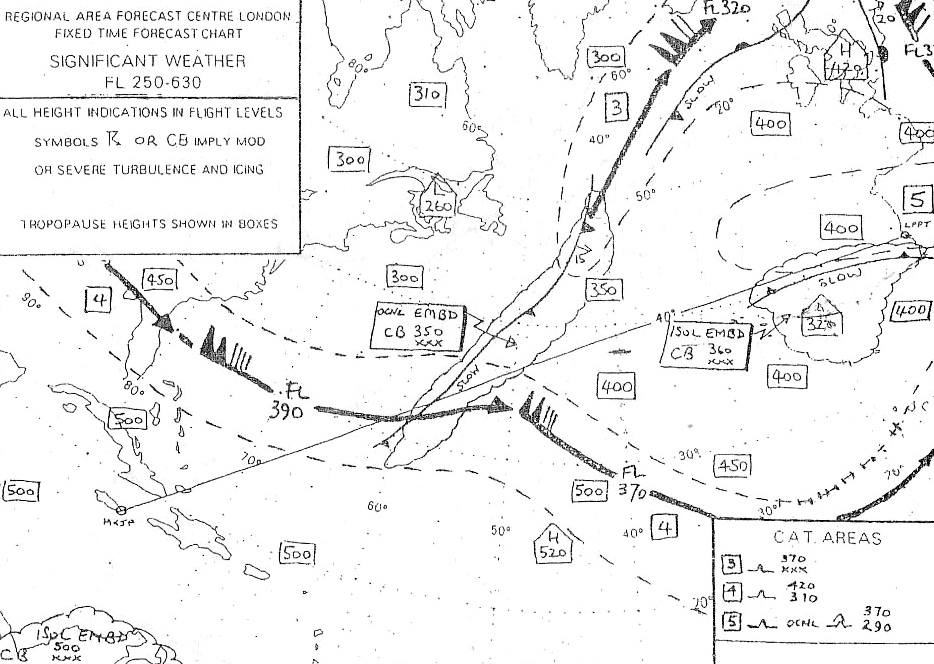
Question 238-20 : In supersonic flight aerofoil pressure distribution is ?
Rectangular
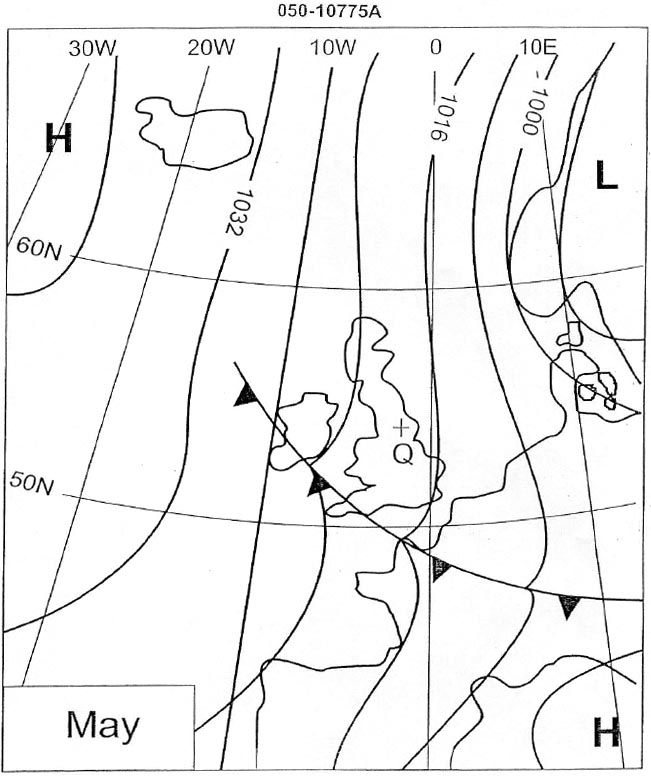
Question 238-21 : Shock stall ?
Occurs when the lift coefficient as a function of mach number reaches its maximum value
Question 238-22 : Which of the following flight phenomena can only occur at mach numbers above the critical mach number ?
Question 238-23 : Which of the following flight phenomena can occur at mach numbers below the critical mach number ?
Dutch roll
Question 238-24 : The mach trim system will ?
Adjust the stabiliser depending on the mach number
Question 238-25 : The mach trim system will prevent ?
Tuck under
Question 238-26 : When air has passed an expansion wave the static pressure is ?
Question 238-27 : The critical mach number of an aeroplane is the free stream mach number that produces the first sign of ?
Local sonic flow
Question 238-28 : In transonic flight the ailerons will be less effective than in subsonic flight because ?
Question 238-29 : Compressibility effects depend on ?
Mach number
Question 238-30 : The formula for the mach number is a= speed of sound ?
Question 238-31 : If the altitude is increased and the tas remains constant in the troposphere under standard atmospheric conditions the mach number will ?
Question 238-32 : Assuming isa conditions climbing at a constant mach number up the tropopause the tas will ?
Question 238-34 : In case of supersonic flow retarded by a normal shock wave a high efficiency low loss in total pressure can be obtained if the mach number in front of the shock is ?
Small but still supersonic
Question 238-35 : The regime of flight from the critical mach number up to approximately m = 1 3 is called the ?
Question 238-36 : Just above the critical mach number the first evidence of a shock wave will appear at the ?
Upper side of the wing

Question 238-37 : Shock induced separation results in ?
Decreasing lift
Question 238-38 : In the transonic range lift will decrease at the shock stall due to the ?
Question 238-39 : Is a transport aeroplane allowed to fly at a higher mach number than the 'buffet onset' mach number in 1g flight ?
Question 238-40 : The mach number is the ratio between the ?
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
9479 Free Training Exam