The ducted fan type tail rotor ? [ Test maintenance ]
Question 52-1 : Uses an aerofoil shaped duct creating thrust is chosen in design solely due to the safety reasons is mounted at the base of the fin allowing lighter supporting structure and to offset the fin to counter tail rotor drift is of simpler design and of a lower cost of manufacture than a traditional tail rotor
 Uses an aerofoil shaped duct creating thrust.
Uses an aerofoil shaped duct creating thrust. Friction controls are usually fitted to ?
Question 52-2 : Both collective and cyclic controls but only the collective friction is adjustable in flight both collective and cyclic controls which are adjustable in flight the collective control only the cyclic control only
 Both collective and cyclic controls, but only the collective friction is adjustable in flight.
Both collective and cyclic controls, but only the collective friction is adjustable in flight. Which of the following statements about the swash plate in a helicopter ?
Question 52-3 : To be able to move or to tilt the swash plate in all directions at least three separate servo units are needed helicopters with a so called artificial feel do not need a swash plate all helicopters are equipped with a swash plate another name for swash plate is spider arm
 To be able to move or to tilt the swash plate in all directions at least three separate servo units are needed.
To be able to move or to tilt the swash plate in all directions at least three separate servo units are needed. The main reason for fitting a rotor brake can be .1 to bring the rotor quickly ?
Question 52-4 : 1 3 3 4 1 3 4 2 4
 1, 3.
1, 3. Rotor brakes are often located ?
Question 52-5 : On the tail rotor drive shaft on the main rotor shaft on a separate drive shaft on the main rotor gear box within the main rotor gearbox
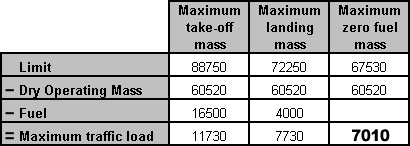 On the tail rotor drive shaft.
On the tail rotor drive shaft. Rotor brake discs are manufactured from ?
Question 52-6 : Steel or carbon fibre alumicnium or steel steel or titanium boron aluminide or titanium
 Steel or carbon fibre.
Steel or carbon fibre. Wear rate of a control rod spherical bearing is ?
Question 52-7 : Exponential progressive constant unpredictable
 Exponential.
Exponential. The purpose of the fixed scissors is to ?
Question 52-8 : Resist the rotational force applied to the lower swashplate in a rotorhead system ensure the wheel remains correctly orientated to the oleo leg in a landing gear act as the lower jaw of the cable cut device on a hoist provide part of feedback mechanism in an auto pilot system
Tail rotors differ from most main rotors in that ?
Question 52-9 : The pitch changes from a negative angle setting to a positive angle setting the tail rotor rotates at a lower speed they always have few blades the lead/lag hinge is incorporated with the flapping hinge
 The pitch changes from a negative angle setting to a positive angle setting.
The pitch changes from a negative angle setting to a positive angle setting. Tail rotors differ from main rotors in that ?
Question 52-10 : They do not provide for blade pitch cyclic variation pitch remains constant throughout all flight regimes they rotate at a lower speed they always have fewer blades
Main rotor droop stops ?
Question 52-11 : Are inactive during flight move to prevent the rotor disc drooping excessively during turbulent conditions preventing damage to the tail cone in flight prevents rotor droop in flight by ensuring the engine provides additional power immediately when required by the rotor prevents engine power reducing below the requirements to sustain rotor rpm
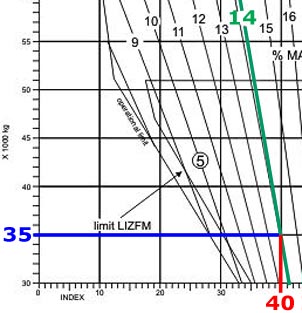 Are inactive during flight.
Are inactive during flight. An unshrouded tail rotor has ?
Question 52-12 : Equal pitch change to all blades different pitch change to each blade cyclic pitch control only rpm control independently of the main rotor
 Equal pitch change to all blades.
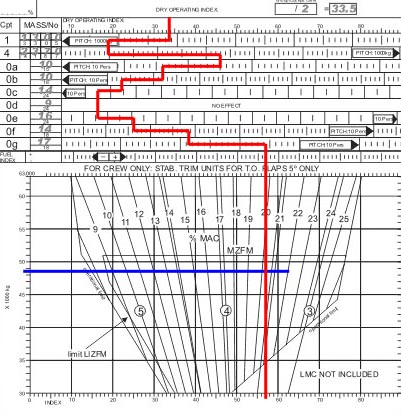
Equal pitch change to all blades. On the diagram the rotating blade pitch control is indicated by the letter . ?
Question 52-13 : D a b c
 D.
D. What is a typical characteristic of a fully articulated rotor system ?
Question 52-14 : The blades are free to flap drag and feather independently of one another the rotor head has flapping hinges only the blades have hinges for all movements the rotor head only has elastomeric hinges for all movements of the blades
 The blades are free to flap, drag and feather independently of one another.
The blades are free to flap, drag and feather independently of one another. Which of the following statements with respect to the rotor brake is correct ?
Question 52-15 : The rotor brake is nearly always implemented as a disc brake the rotor brake is nearly always implemented as a drum brake the rotor brake always slows down the drive shaft between the engine s and the main gear box a hydraulically actuated rotor brake is connected to the same hydraulic system as the flight controls in order to ensure the necessary reliability
 The rotor brake is nearly always implemented as a disc brake.
The rotor brake is nearly always implemented as a disc brake. A rotor is fully articulated when ?
Question 52-16 : The blades each have the possibility to flap drag and feather separately the rotor head has hinges for flapping as well as dragging the blades have been mounted flexibly with regard to flapping and dragging the rotor has more than two blades that have separate flapping and feathering hinges
 The blades each have the possibility to flap, drag and feather separately.
The blades each have the possibility to flap, drag and feather separately. The chord length of the blades of a ducted tail rotor fenestron is ?
Question 52-17 : Smaller than that of a classic tail rotor the same as that of a classic tail rotor greater than that of a classic tail rotor depends on the type of material used
 Smaller than that of a classic tail rotor.
Smaller than that of a classic tail rotor. An elastomeric bearing flapping hinge in the rotor head ?
Question 52-18 : Contributes to a reduced maintenance effort allows larger blade flapping angles allows for larger forward speeds is utilised to absorb the loads on the rotor blades arising from vertical gusts
 Contributes to a reduced maintenance effort.
Contributes to a reduced maintenance effort. What are elastomeric bearing hinges in a rotor head ?
Question 52-19 : Flexible sections accomplishing the functions of flapping dragging and feathering hinges self lubricating hinges bending plastic parts rubber flapping and dragging hinges
 Flexible sections accomplishing the functions of flapping, dragging and feathering hinges.
Flexible sections accomplishing the functions of flapping, dragging and feathering hinges. Intermediate or angle gearboxes are used to ?
Question 52-20 : Change the direction and sometimes the speed of the tail rotor drive change the direction of the tail rotor drive only change the speed of the tail rotor drive only mount the tail rotor
 Change the direction and sometimes the speed of the tail rotor drive.
Change the direction and sometimes the speed of the tail rotor drive. To engage the main rotor drive prior to flight on a helicopter fitted with a ?
Question 52-21 : Smoothly accelerate the engine with rotor brake selected off accelerate the engine above rotor speed decelerate the engine then accelerate again until engine and rotor speeds are matched de select the free wheel and engage drive accelerate the engine until engine and rotor speed are equal then engage the clutch using either a mechanical lever or an electrical switch
 Smoothly accelerate the engine with rotor brake selected off.
Smoothly accelerate the engine with rotor brake selected off. The tail rotor gearbox changes direction of drive ?
Question 52-22 : Through 90° reduces rotational speed and provides facilities for tail rotor control through minus 90° and increases rotational speed and increases rotational speed and provides facilities for tail rotor control maintaining a constant speed
 Through 90°, reduces rotational speed and provides facilities for tail rotor control.
Through 90°, reduces rotational speed and provides facilities for tail rotor control. The purpose of a clutch in a helicopter transmission system is to ?
Question 52-23 : Permit the engine to be started with a low inertial loading permit the rotor to rotate freely during autorotation prevent the rotor turning in the wind when parked on the ground disengage the tail rotor drive in the event of a malfunction
 Permit the engine to be started with a low inertial loading.
Permit the engine to be started with a low inertial loading. Rotational drive from the gearbox to the rotorhead is transmitted by the ?
Question 52-24 : Main drive shaft scissors swashplate assembly pitch change arms
 Main drive shaft.
Main drive shaft. Intermediate or angle gearboxes are used to ?
Question 52-25 : Change the direction and speed of the tail rotor drive change the direction only of the tail rotor drive change the speed only of the tail rotor drive allow the incorporation of autopilot inputs into the tail rotor
 Change the direction and speed of the tail rotor drive.
Change the direction and speed of the tail rotor drive. In a free turbine helicopter installation ?
Question 52-26 : There is no need for a clutch between the engine and the transmission a free wheel is required between the compressor and the turbine the main rotor drive and the compressor are on a common shaft there must be a clutch between the engine and transmission
 There is no need for a clutch between the engine and the transmission.
There is no need for a clutch between the engine and the transmission. Helicopters which utilise a ''v' belt to transmit the drive from the engine to ?
Question 52-27 : A manual clutch an automatic system to ensure belt tension remains constant irrespective of temperature a means by which the engineer can set the belt tension an automatic clutch
 A manual clutch.
A manual clutch. Freewheel units between engine and main rotor gearbox are in most cases ?
Question 52-28 : The main rotor gearbox lubrication system the engine lubrication system an independent lubrication system driven by the main rotor gearbox an independent system driven by either the engine or an electrically driven pump
 The main rotor gearbox lubrication system.
The main rotor gearbox lubrication system. For a free power turbine engine ?
Question 52-29 : The turbine driving the main rotor transmission is mechanically independent from the gas generator the compressor driving the main transmission is mechanically independent from the power turbine the gas generator is free to run at a constant speed while the power turbine changes speed in response to changes in drag on the main rotor blades pilot control of the engine is limited to the selection of off ground idle and flight leaving the engine to automatically respond to rotor demands
 The turbine driving the main rotor transmission is mechanically independent from the gas generator.
The turbine driving the main rotor transmission is mechanically independent from the gas generator. Clutches are located in the drive between the engine and the main transmission ?
Question 52-30 : Helicopters with piston or direct drive gas turbine engines all helicopters helicopters fitted with piston engines only helicopters with free power turbine engines only
 Helicopters with piston or direct drive gas turbine engines.
Helicopters with piston or direct drive gas turbine engines. A tail rotor drive shaft running between two engines should be ?
Question 52-31 : Protected by a firewall mounted to allow for expansion mounted on its own bearing hangers the first being directly behind the main rotor gearbox protected by the engine fire extinguishing system
 Protected by a firewall.
Protected by a firewall. What is the purpose of the freewheel unit in the rotor drive system ?
Question 52-32 : To disconnect the failed engine from the main and tail rotor drive to enable the rotor to rotate freely for autorotation to be able to start the engine s without starting to turn the rotor to be able to disconnect the main rotor from the drive system when the engine fails
 To disconnect the failed engine from the main and tail rotor drive.
To disconnect the failed engine from the main and tail rotor drive. Does the freewheel unit is necessary for helicopter with free turbine engine ?
Question 52-33 : Yes no not with new generation engines but only for multi engined helicopters no
 Yes.
Yes. A snatch engagement of a freewheel unit ?
Question 52-34 : May result in the shearing of the engine drive shaft is normal engagement is absorbed by flexible couplings on the engine drive shaft will cause the freewheel to ratchet until the pilot recovers the situation
 May result in the shearing of the engine drive shaft.
May result in the shearing of the engine drive shaft. A mercury clutch ?
Question 52-35 : Utilises the weight of the mercury to provide the centrifugal force to act on the clutch shoes is not used in helicopters due to the danger of mercury contamination of aluminium uses the liquid mercury as a hydraulic fluid is not used in helicopters due to the high weight of mercury
 Utilises the weight of the mercury to provide the centrifugal force to act on the clutch shoes.
Utilises the weight of the mercury to provide the centrifugal force to act on the clutch shoes. The input and output speeds of an intermediate gearbox ?
Question 52-36 : Differ to counter the effects of vibration differ to establish the speed for the tail rotor are the same are variable to provide varying thrust from the tail rotor to counteract torque loads from the main rotor system
 Differ to counter the effects of vibration.
Differ to counter the effects of vibration. Tail rotors rotate ?
Question 52-37 : At a greater speed than the main rotor and at a different speed than the drive shaft and intermediate gearbox at the same speed as the shafts and gear boxes at a greater speed than the main rotor and the tail rotor drive shafts at a lower speed than the main rotor
 At a greater speed than the main rotor and at a different speed than the drive shaft and intermediate gearbox.
At a greater speed than the main rotor and at a different speed than the drive shaft and intermediate gearbox. Why are one or more flexible couplings usually incorporated in the tail rotor ?
Question 52-38 : To absorb the angular differences arising from bending of the tail to absorb quick power changes to prevent vibrations to prevent torsion of the shafts
 To absorb the angular differences arising from bending of the tail.
To absorb the angular differences arising from bending of the tail. Metal tail rotor drive shafts are normally manufactured from ?
Question 52-39 : Aluminium or steel tubing aluminium tubing only steel bar titanium and steel tubing
 Aluminium or steel tubing.
Aluminium or steel tubing. On the diagram the flapping hinge is indicated by number ?
Question 52-40 : 1 2 3 4
 1.
1. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2039 Free Training Exam
