The most common sensors interfacing a fms to compute the aircraft position ? [ Exam pilot ]
Question 70-1 : 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 1 3 4
 1, 2.
1, 2. The fms provides the following functions .1 radio tuning.2 fuel management.3 ?
Question 70-2 : 1 2 3 3 4 2 3 4 1 2 4
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. Concerning the fms flight management system the cost index is determined by ?
Question 70-3 : Aircraft operating cost by fuel cost fuel cost by aircraft operating cost aircraft cruise speed by fuel cost fuel cost by aircraft cruise speed
 Aircraft operating cost by fuel cost.
Aircraft operating cost by fuel cost. Concerning the fms flight management system entering a high cost index results ?
Question 70-4 : High airspeed and high fuel trip maximum range airspeed minimum trip fuel minimum airspeed
Concerning the fms flight management system entering a cost index of zero ?
Question 70-5 : Maximum range airspeed maximum cruising airspeed minimum range airspeed minimum airspeed
 Maximum range airspeed.
Maximum range airspeed. The fms is approved for localizer approaches ?
Question 70-6 : If the localizer signals are used by the fms if the gps only is used as navigation sensor if the gps and dmes only are used as combined navigation sensors if the dmes only are used as navigation sensors
Concerning the fms flight management system entering a cost index of zero ?
Question 70-7 : Results in minimum trip fuel results in maximum trip fuel does not influence fuel consumption modifies only cruising airspeed
 Results in minimum trip fuel.
Results in minimum trip fuel. The fms is approved to provide guidance for the following approaches .1 rnav ?
Question 70-8 : 1 3 2 4 1 3 4 1 2
 1, 3.
1, 3. The fms is approved to provide guidance for the following approaches .1 rnav ?
Question 70-9 : 1 4 2 3 1 2 4 1 3 4
 1, 4.
1, 4. The fms is approved to provide guidance for the following approaches ?
Question 70-10 : Non precision approaches non precision approaches and ils cat i precision approaches only non precision and precision approaches precision approaches limited to cat ii
 Non precision approaches.
Non precision approaches. The fms navigation database includes the following data .1 obstacles.2 ?
Question 70-11 : 2 3 5 1 2 3 1 3 5 1 2 4
 2, 3, 5.
2, 3, 5. The purpose of the fms temperature compensation function is ?
Question 70-12 : To provide compensated altitudes for temperatures different from standard atmosphere along the vertical approach profile to provide compensated temperatures at the waypoints along the vertical approach profile to provide the destination airport air temperature to provide the destination airport or runway elevation
 To provide compensated altitudes for temperatures different from standard atmosphere along the vertical approach profile.
To provide compensated altitudes for temperatures different from standard atmosphere along the vertical approach profile. The fms provides the following functions .1 lateral and vertical flight plan ?
Question 70-13 : 1 3 1 2 3 1 3 4 4
 1, 3.
1, 3. Concerning the fms the parameters used to work out the vertical flight profile ?
Question 70-14 : 1 2 3 1 2 3 5 1 2 5 3 4 5
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. Components of the fms are .1 cdu control and display unit .2 database.3 fmc ?
Question 70-15 : 1 2 3 1 2 4 5 1 3 3 4
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. The fms provides the following functions .1 vertical flight plan management .2 ?
Question 70-16 : 1 2 3 1 2 4 2 3 4 1 3 4
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. The fmc determines and update present aircraft position from the following ?
Question 70-17 : 1 2 3 1 2 4 1 2 3 4 3
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. The fmc determines and update present aircraft position from the following ?
Question 70-18 : 2 3 4 1 2 4 2 4 1 3
 2, 3, 4.
2, 3, 4. The fms enables to fly an optimum flight profile for this the fmc flight ?
Question 70-19 : 1 2 3 5 1 2 5 2 3 4 1 3 5
The fms flight plan or leg page displays the following parameters relative to ?
Question 70-20 : 2 3 4 1 3 4 1 2 1 2 3 4
 2, 3, 4.
2, 3, 4. The fms provides the following functions .1 traffic advisories emission.2 ?
Question 70-21 : 3 4 1 3 4 1 2 3 1 4
 3, 4.
3, 4. The fms flight plan or leg page displays the following parameters relative to ?
Question 70-22 : 1 4 1 3 3 4 1 2 4
 1, 4.
1, 4. For most fms the fuel prediction function which computes the remaining fuel ?
Question 70-23 : 2 1 3 2 4 3
 2.
2. For most fms the fuel prediction function which computes the remaining fuel ?
Question 70-24 : 4 1 4 3 3 1 2
 4.
4. The duration of a fms navigation database loaded before expiring is ?
Question 70-25 : 28 days 15 days 2 months 3 months
 28 days.
28 days. The role of the fms is to .1 aid the crew with navigation.2 shut down the ?
Question 70-26 : 1 4 5 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 1 3 4
 1, 4, 5.
1, 4, 5. The role of the fms is to aid the flight crew with .1 immediate actions in ?
Question 70-27 : 2 3 2 3 4 3 4 1 2
 2, 3.
2, 3. In a fms mcdus are used pre flight to manually initialise with dispatch ?
Question 70-28 : 1 4 2 1 3 2 3 4
 1, 4.
1, 4. The 'overfly' symbol related to a waypoint on an fms page indicates that ?
Question 70-29 : The aircraft is required to pass directly over this waypoint a time estimate is given for this waypoint a turn anticipation is permited a fuel prediction is given for this waypoint
 The aircraft is required to pass directly over this waypoint.
The aircraft is required to pass directly over this waypoint. The fms required time of arrival rta function can provide ?
Question 70-30 : A speed target to satisfy a time constraint entered at a flight plan waypoint a time slot computed for the arrival time at destination using the current aircraft speed and speed constraints along the flight plan a time prediction at the active to waypoint complying with the wind computation a time prediction at the flight plan waypoints based on the current speed and speed constraints along the flight plan
 A speed target to satisfy a time constraint entered at a flight plan waypoint.
A speed target to satisfy a time constraint entered at a flight plan waypoint. The fuel management performed by most fms along the flight plan is considered as ?
Question 70-31 : A function which helps the crew to estimate the remaining fuel quantity along the flight plan but should not be considered as an accurate and reliable source an accurate function which can be considered as the prime source to determine the remaining fuel quantity along the flight plan an accurate and very reliable function providing that the fuel on board quantity has been properly initialized by the crew before start up the prime source to manage the fuel consumption along the flight
 A function which helps the crew to estimate the remaining fuel quantity along the flight plan but should not be considered as an accurate and reliable source.
A function which helps the crew to estimate the remaining fuel quantity along the flight plan but should not be considered as an accurate and reliable source. Some of the fms have a navigation mode called dead reckoning mode dr computing ?
Question 70-32 : A back up navigation mode to compute a fms position when the other navigation sensors are no longer operating an operating mode used to intercept radials to or from a flight plan waypoint a navigation mode used to monitor the fms position the normal navigation mode for fms which do not use inertial navigation systems ins to compute the aircraft position
 A back up navigation mode to compute a fms position when the other navigation sensors are no longer operating.
A back up navigation mode to compute a fms position when the other navigation sensors are no longer operating. The fms lateral offset function consists in ?
Question 70-33 : Flying along the flight plan legs with a constant right or left offset manually entered on the fms cdu displaying the lateral cross track deviation xtk of the aircraft according to the active flight plan leg creating a new waypoint using a reference flight plan waypoint and a distance from this waypoint along the flight plan legs flying a fms selected lateral pattern used for search and rescue operations
 Flying along the flight plan legs with a constant right or left offset manually entered on the fms cdu.
Flying along the flight plan legs with a constant right or left offset manually entered on the fms cdu. The fms navigation database includes the following data .1 airports.2 ?
Question 70-34 : 1 3 4 1 2 3 2 5 1 3 4 5
 1, 3, 4.
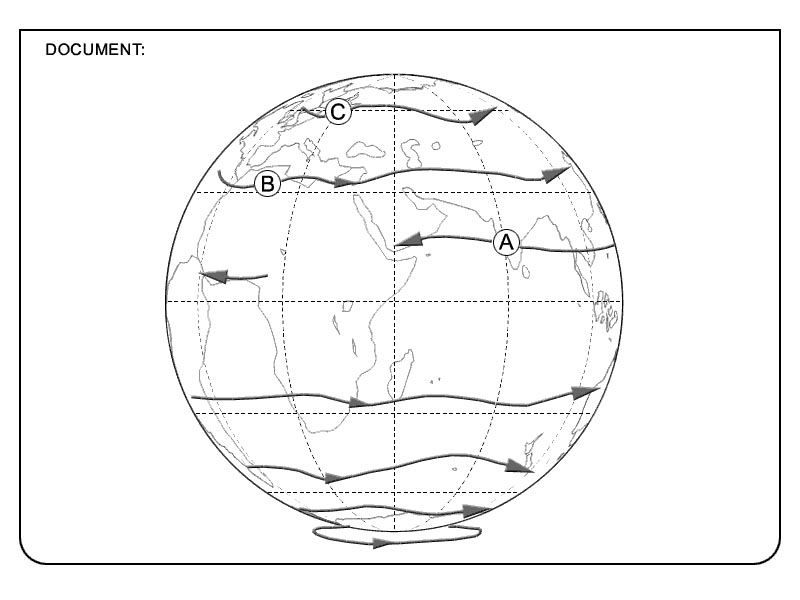
1, 3, 4. The most common sensors interfacing a fms to compute the aircraft position ?
Question 70-35 : 1 3 1 2 3 2 3 1 4
 1, 3.
1, 3. For a fms designed with the vertical navigation vnav capability coupled to the ?
Question 70-36 : 2 3 1 2 1 3 2
 2, 3.
2, 3. The fms navigation database includes the following data .1 obstacles.2 ?
Question 70-37 : 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 4 1 3 5
 2, 3, 4, 5.
2, 3, 4, 5. The fms provides the following functions .1 aid for fuel management.2 lateral ?
Question 70-38 : 1 2 4 1 2 3 2 3 3 4
 1, 2, 4.
1, 2, 4. The fms cross track xtk is ?
Question 70-39 : The abeam distance error to the left or right from the desired flight plan leg to the aircraft position the angular distance error to the left or right from the desired track dtk to the aircraft track tk the distance error between the fms computed position and the irs computed position the distance error between the fms computed position and the gps computed position
 The abeam distance error, to the left or right from the desired flight plan leg to the aircraft position.
The abeam distance error, to the left or right from the desired flight plan leg to the aircraft position. The fms vertical navigation management is generally performed based on ?
Question 70-40 : The baro altitude input from the adc the gps altitude computed by the gps receiver a mix of baro and gps altitudes the geometric altitude input from the terrain awareness and warning system taws
 The baro altitude input from the adc.
The baro altitude input from the adc. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2759 Free Training Exam
