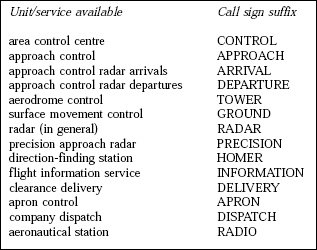
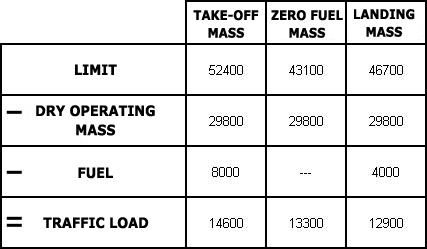
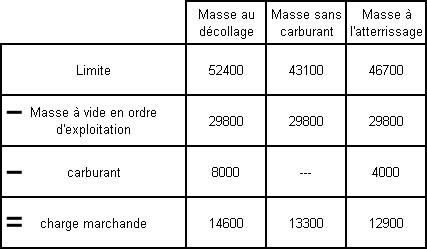
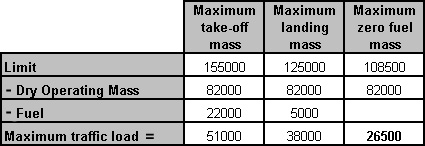
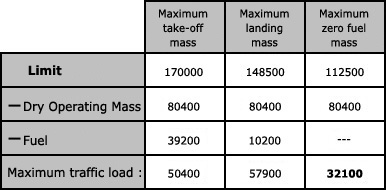
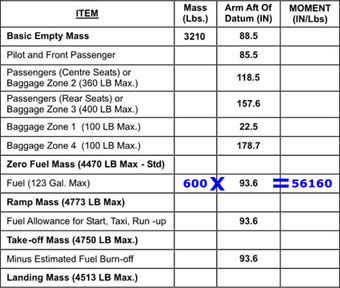
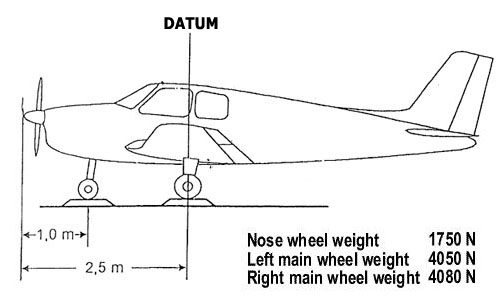
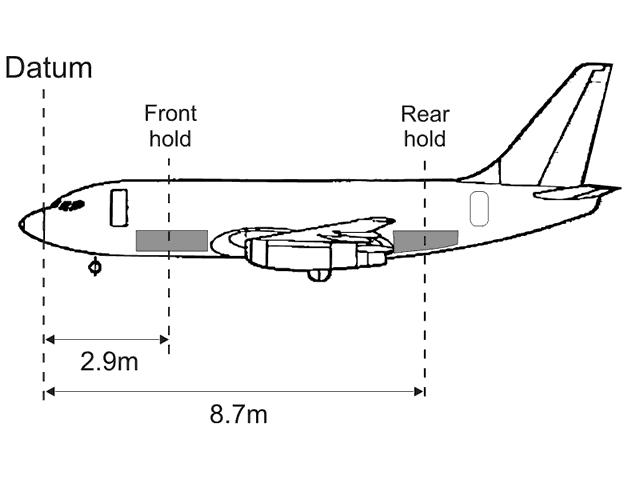
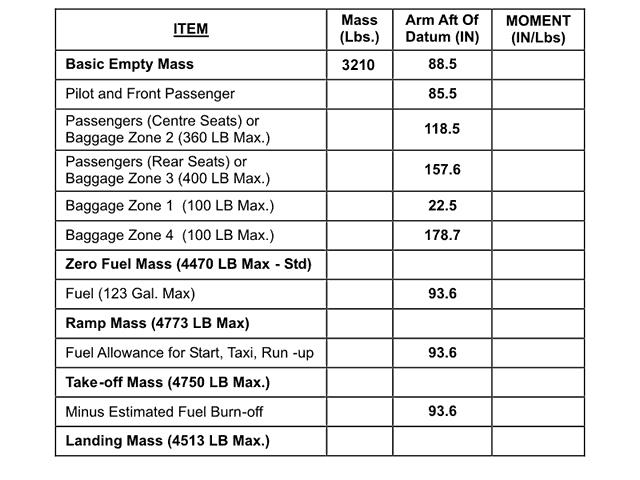
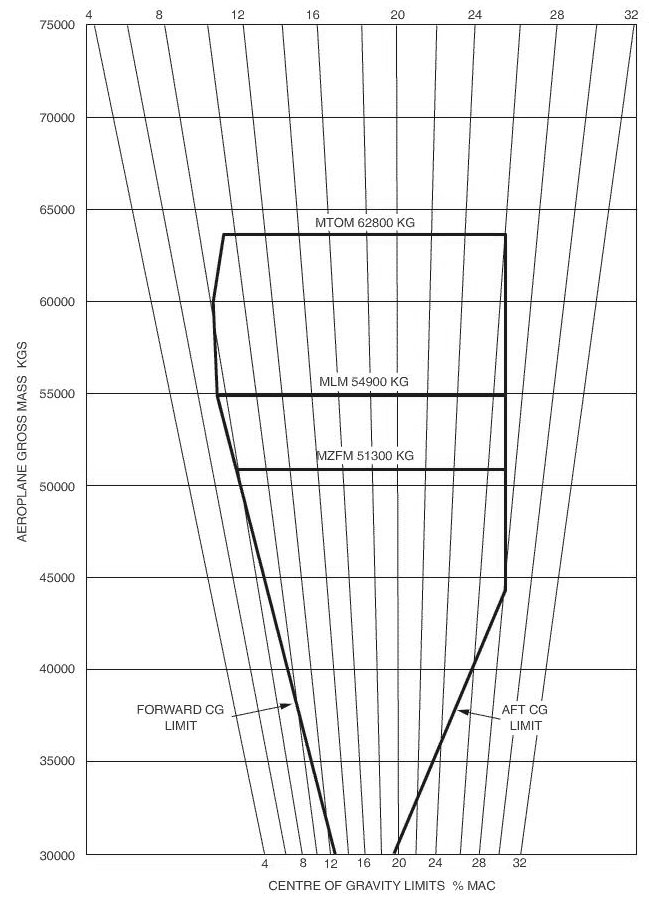
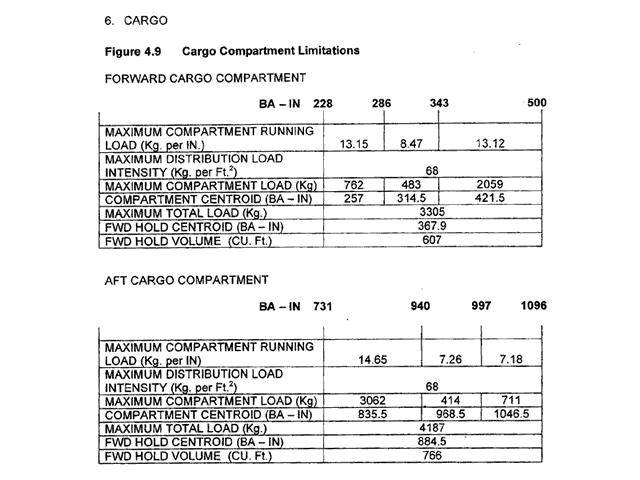
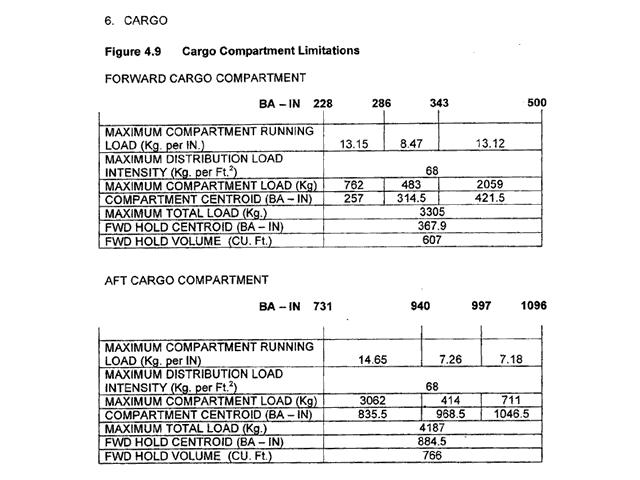
Question 11-1 : Instrument departure procedure wind correction .flying an instrument departure procedure pilots are expected to ? [ Correction orientation ]
Correct the track for known wind to remain within the protected airspace

Question 11-2 : Instrument departure procedures obstacle clearance .the minimum obstacle clearance at the departure end of runway der equals ?
Question 11-3 : 'instrument runways' are the following runways intended for the operation of aircraft using instrument approach procedures ?
Non precision approach runways precision approach runways category i ii and iii
Question 11-5 : Minimum level ifr .over high terrain or mountainous areas where no minimum flight altitude has been established flights in accordance with ifr shall be flown at a level which is at least ?
Question 11-6 : Oca.an oca is referenced to ?
Question 11-7 : Ssr transponder.pilots shall not squawk ident unless they ?
Question 11-8 : Ssr transponder.when the aircraft carries serviceable mode c transponder the pilot shall continuously operate this mode ?
Question 11-9 : Ssr transponder.when acknowledging mode / code setting instructions pilots shall ?
Question 11-10 : Ssr transponder.when an aircraft is subjected to unlawful interference the pilot in command shall indicate the situation by setting the transponder to mode a code ?
A 7500
Question 11-11 : Ssr transponder.ssr means ?
Question 11-12 : Ssr transponder.when an aircraft carries a serviceable transponder the pilot shall operate the transponder ?
Question 11-13 : Ssr special codes.atc has assigned you the transponder code 5320 in case of loosing two way radio communication you have to squawk ?
Question 11-14 : Standard instrument departure procedures straight departures .a straight departure is one in which the initial departure track does not deviate from the alignment of the extended runway centre line by more than ?
Question 11-15 : The tolerance value used to determine that mode c derived level information displayed to the controller is accurate shall be ?
+/ 300 ft
Question 11-16 : The visual contact with the runway is lost on the down wind leg while circling to land following an instrument approach you have to initiate a go around ?
Make an initial climbing turn towards the runway and initiate the missed approach procedure
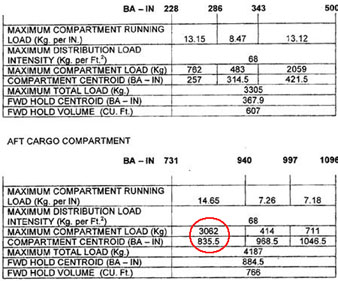
Question 11-17 : Ssr transponder.when the transponder appears to be unserviceable prior to departure and restore is impossible than ?
Departure to the nearest suitable airport where repair can be effected is allowed
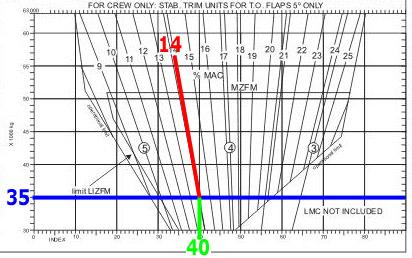
Question 11-18 : Ssr transponder.which code shall be used on mode 'a' to provide recognition of an aircraft subjected to unlawful interference ?
Question 11-19 : Ssr transponder.which code shall be used on mode 'a' to provide recognition of an emergency aircraft ?
Question 11-20 : Which of the following correctly lists special purpose codes that are to be used in conjunction with secondary surveillance radar ssr ?
Question 11-21 : When should the latest qnh altimeter setting for the aerodrome be obtained ?
Question 11-22 : When should the flight crew shall be provided with the transition level ?
Question 11-23 : The calculated height of the transition altitude shall be rounded up to the next full ?
Question 11-24 : Omnidirectional departure normally allow departure in any direction if any restriction exist the restricted areas/sectors are described by means of ?
Question 11-25 : Unless otherwise published or instructed by atc all turns after initial entry into the holding pattern shall be made into which direction ?
Question 11-26 : Altimeter pressure settings provided to aircraft shall be rounded ?
Question 11-27 : For the construction of precision approaches which is the operationally preferred glide path angle ?
Question 11-28 : In an instrument approach procedures what is the name of segment connecting initial and final approach segments ?
Intermediate segment
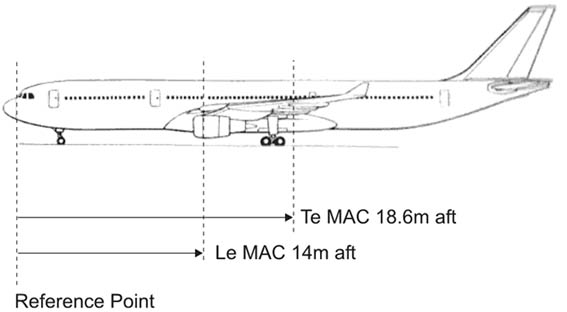
Question 11-29 : The fixes connecting the arrival segment and final approach fix or point are ?
Question 11-30 : When should the flight crew shall be provided with the transition level ?
Before beginning the initial approach to an aerodrome
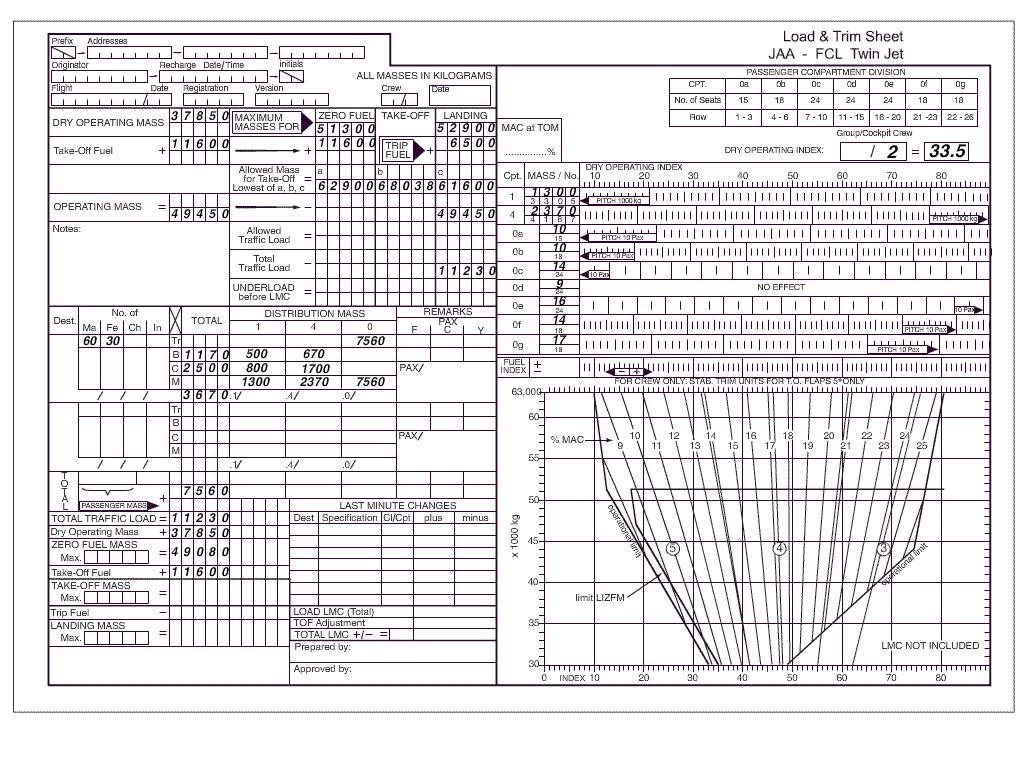
Question 11-31 : Approach segments .in an instrument approach procedures during the intermediate segment ?
The aircraft speed and configuration should be adjusted to prepare the aircraft for final approach
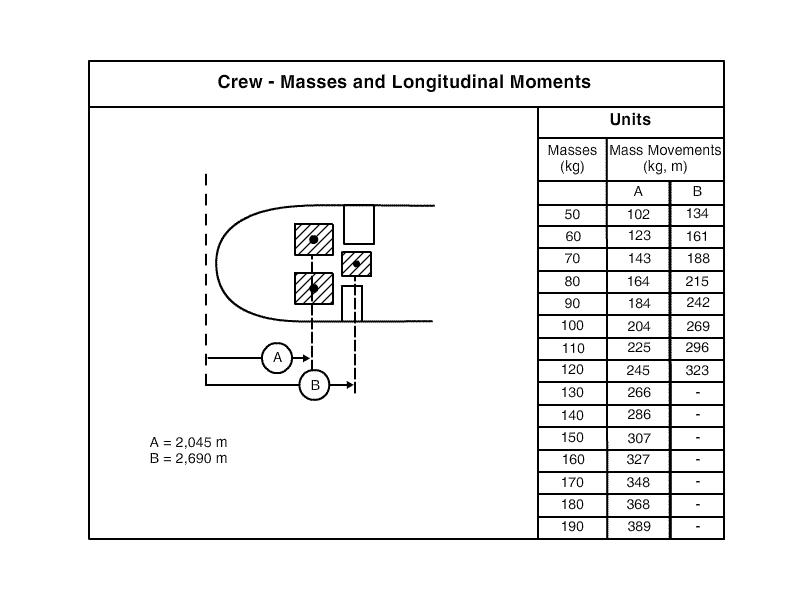
Question 11-32 : Approach segments .in an instrument approach procedures during the initial segment ?
The aircraft leaves the en route structure and is manoeuvring to enter the intermediate approach.segment
Question 11-33 : According to icao 8168 regarding omnidirectional departures you would expect ?
No navigation aids and sectors to be avoided
Question 11-34 : What is the purpose of the commission regulation eu no 965/2012 of 5 october 2012 ?
Lay down detailed rules for commercial air transport operations with aeroplanes and helicopters including ramp inspections of aircraft of operators under the safety oversight of another state when landed at aerodromes located in the territory subject to the provisions of the treaty
Question 11-35 : The cruising levels at which a flight or a portion of a flight is to be conducted shall be in terms of… ?
Flight levels if the flight is at or above the lowest usable flight level
Question 11-36 : The cruising levels at which a flight is conducted shall be expressed in terms of… ?
Altitudes for flights at or below the transition altitude
Question 11-37 : What is the turn made by an aircraft during the initial approach to the runway between the end of the outbound track and the beginning of the intermediate or final approach track where the tracks are not reciprocal ?
Base turn
Question 11-38 : A turning departure is one in which the initial departure track deviates from the alignment of the extended runway centre line by more than ?
15°
Question 11-39 : Standard instrument departure procedures – straight departures – in a straight departure the initial track does not deviate from the alignment of the extended runway centre line by more than… ?
15 degrees
Question 11-40 : Omnidirectional departures normally allow departures in any direction if any restrictions exist the restricted sectors are described by means of ?
Bearings and distance

Our Mock Exams
They faithfully reproduce the look and experience of official exams, allowing you to become familiar with the real conditions, both visually and functionally. This immersive approach helps reduce stress and optimize preparation, providing all the tools needed to succeed in the final exam.
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
399 Free Training Exam Other source study: Afis exam examen 11