Sign up to unlock all our services and 15164 corrected and explained questions.
Question 115-1 : Route manual chart e hi 4 caa edition..the radio navigation aid at st dizier 48°38n 004°53'e is a.. err a 033 342 ? [ Training professional ]
Question 115-2 : Route manual chart e hi 4..an appropriate flight level for flight on airway ur1 from ortac 50°00'n 002°00'w to midhurst mid 114.0 51°03'n 000°37'w is.. err a 033 344 ?
Question 115-3 : Use route manual chart e hi 4 caa edition..an aircraft has to fly from salzburg 48°00.2'n 012°53.6'e to klagenfurt 46°37.5'n 014°33.8'e..which statement is correct.. err a 033 367 ?
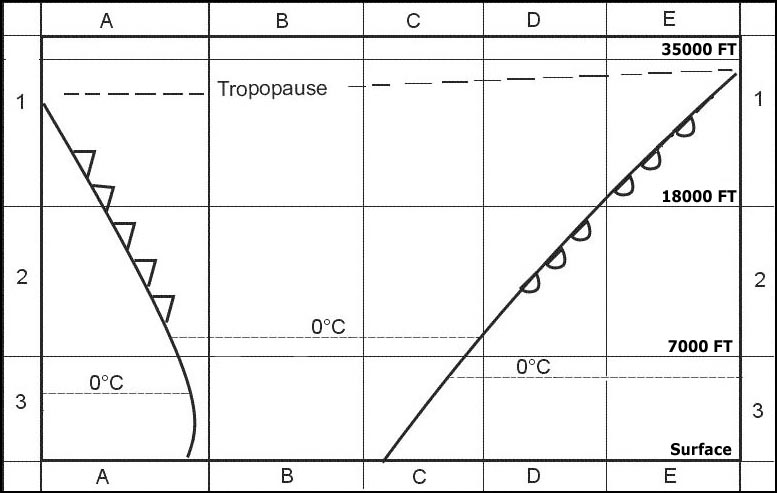
The figure 13.4 means that the minimum grid safe altitude in this sector is 13400 ft above msl.
Question 115-4 : Route manual chart sid paris charles de gaulle 20 3..planning a ifr flight from paris charles de gaulle to london heathrow.find the elevation of the departure aerodrome.. err a 033 370 ?
Question 115-5 : Use route manual chart e lo 1.what is the maximum authorised altitude maa on airway w911d from dean cross 115.2 dcs 54°43'n 003°20'w° to newcastle 114.25 new 55°02'n 001°41'w .. err a 033 373 ?
Question 115-6 : Route manual chart london heathrow ils dme rwy 09l 11 2. the decision altitude da for a ils straight in landing is .. err a 033 374 ?
Question 115-7 : An airway is marked 3500t 2100 a. this indicates that ?
The minimum obstruction clearance altitude moca is 3500 ft.
Question 115-8 : Route manual star chart for london heathrow 10 2d..the minimum holding altitude mha and maximum holding speed ias at mha at ockham ock 115.3 are.. err a 033 381 ?
7000 ft and 220 kt.
Question 115-9 : Route manual sid charts for zurich 10 3..which is the correct albix departure via aarau for runway 16.. err a 033 385 ?
Question 115-10 : Route manual chart e hi 5 caa edition.the first lowest available flight level for flight on airway ug5 from mende nasbinals men 115.3 44°36'n 003°10'e to gaillac gai 115.8 43°57'n 001°50'e is .. err a 033 399 ?
Question 115-11 : For this question, use route manual chart e hi 1.what is the average magnetic course from aberdeen 57°19'n 002°16'w to tiree 56°30'n 006°53'w .. err a 033 400 ?
Question 115-12 : Route manual star 10 2 and instrument approach chart 11 4 ils dme rwy 27r for london heathrow.planning an ifr flight from paris to london heathrow.name the identifier and frequency of the initial approach fix iaf of the big 2a arrival route.. err a 033 401 ?
Question 115-13 : Use route manual chart e hi 2..an aircraft has to fly on airways from sveda 56°10'n 012°34'e to skara 58°23'n 013°15'e. which of the following is the correct route.. err a 033 409 ?
Question 115-14 : An airway is marked fl 80 1500 a. this indicates that ?
Question 115-15 : Route manual chart e hi 4 caa edition.the radio navigation aid on airway ug4 at luxeuil 47°41'n 006°18'e is a.. err a 033 424 ?
Question 115-16 : Route manual chart e lo 1. the radio navigation aid at shannon 52°43'n 008°53'w is .. err a 033 425 ?
Question 115-17 : Use route manual chart e hi 2..an aircraft has to fly from the beacon tno 55°46'n 011°26'e on a direct route to the beacon har 57°50'n 012°42'e..what is the magnetic track and distance for this flight.. err a 033 426 ?
018°/131 nm.
Question 115-18 : Use route manual chart e hi 1.an aircraft has to fly from the airport at aberdeen 57°19'n 002°16'w to the airport at benbecula 57°29'n 007°22'w..given.time to climb 11 min..time to descend is 15 min.toc is at 3w.tod is at 6w..tas 210 kt still air.find the total journey time. toc/top top of ?
Question 115-19 : For this question use route manual chart e hi 2.the identifier of the radio navigation aid at 56°07'n012°58'e is.. err a 033 429 ?
Question 115-20 : Route manual chart e lo 1.the radio navigation aid at belfast city 54°37'n 005°53'w is .. err a 033 431 ?
Question 115-21 : Route manual chart e lo 2. the minimum enroute altitude mea that can be maintained continuously on airway g4 from jersey jsy 112.2 49°13'n 002°03'w to lizad 49°35'n 004°20'w is .. err a 033 432 ?
Question 115-22 : Route manual chart amsterdam schiphol ils dme rwy 22 11 6..the missed approach procedure is to climb to an alitude of i... on a track of ii..... err a 033 440 ?
Question 115-23 : Route manual chart e hi 4 caa edition.the magnetic course/distance from dinkelsbuhl dkb 117.8 49°09'n010°14'e to erlangen erl 114.9 49°39'n011°09'e on airway ur11 is.. err a 033 442 ?
Question 115-24 : Route manual chart e lo 6. an appropriate flight level for flight on airway r10 from montmedy mmd 109.4 49°24'n 005°08'e to chatillon ctl 117.6 49°08'n 003°35'e is .. err a 033 445 ?
Question 115-25 : Route manual chart e lo 1.the radio navigation aid at topcliffe 54°12'n 001°22'w is a.. err a 033 448 ?
Question 115-26 : Route manual chart e lo 1..the minimum enroute altitude that can be maintained continuously on airway g1 from strumble stu 113.1 52°00'n 005°02'w to brecon bcn 117.45 51°43'n 003°16'w is .. err a 033 451 ?
Fl110.
Question 115-27 : On an ifr navigation chart, in a 1° quadrant of longitude and latitude, appears the following information '80'..this means that within this quadrant ?
Question 115-28 : Route manual chart e hi 4 caa edition. planning a ifr flight from paris charles de gaulle n49 00.9 e002 36.9 to london heathrow n51 29.2 w000 27.9..find the average true course from paris to london... err a 033 468 ?
Question 115-29 : Route manual star charts for munich 10 2b..the correct arrival route and initial approach fix iaf for an arrival from the west via tango for runway 08 l/r is.. err a 033 479 ?
Question 115-30 : For this question use trm, athinai hellinikon approach chart 29 1.what is the total distance when following the vfr routeing from 'abeam patroklos' to hellinikon.. err a 033 485 ?
Question 115-31 : Use route manual chart e lo 1.an appropriate flight level for flight on airway a2 from talla 113.8 tla 55°30'n 003°21'w to dean cross 115.2 dcs 54°43'n 003°20'w is.. err a 033 492 ?
Fl90
Question 115-32 : Use route manual chart e hi 1..the direct distance from tiree 117.7 tir 56°30'n006°53'w to inverness 109.2 ins 57°32'n004°03'w is.. err a 033 508 ?
Question 115-33 : Route manual chart e lo 5..the vor and tacan on airway g9 at osnabruck 52°12'n 008°17'e are.. err a 033 511 ?
Question 115-34 : Use route manual chart e lo 1.the magnetic course / distance from dean cross 115.2 dcs 54°43'n 003°20'w° to pole hill 112.1 pol 53°45'n 002°06'w on airway a2 is.. err a 033 517 ?
Question 115-35 : Route manual chart london heathrow ils dme rwy 09r 11 1..the minimum descent altitude mda for an ils glide slope out, is.. err a 033 519 ?
Question 115-36 : Route manual sid chart 20 3 for paris charles de gaulle. planning an ifr flight from paris to london.determine the distance of the departure route abb 8a.. err a 033 523 ?
Question 115-37 : Use route manual chart e hi 1..the initial magnetic course from tiree 117.7 tir 56°30'n006°53'w direct to inverness 109.2 ins 57°32'n004°03'w is.. err a 033 524 ?
064°.
Question 115-38 : Use route manual chart e lo 1..what is the minimum enroute altitude mea on airway w911d from dean cross 115.2 dcs 54°43'n 003°20'w° to newcastle 114.25 new 55°02'n 001°41'w .. err a 033 535 ?
Question 115-39 : Route manual chart e hi 4 caa edition.of the following, the preferred airways routing from clacton cln 114.55 51°51'n 001°09'e to dinard din 114.3 48°35'n 002°05'w above fl245 is.. err a 033 555 ?
Question 115-40 : Route manual sid chart 20 3 for paris charles de gaulle.planning an ifr flight from paris charles de gaulle rwy 27 to london..given.distance from paris charles de gaulle to top of climb 50 nm.determine the distance from the top of climb toc to abb 116.6 .. err a 033 558 ?
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
4559 Free Training Exam