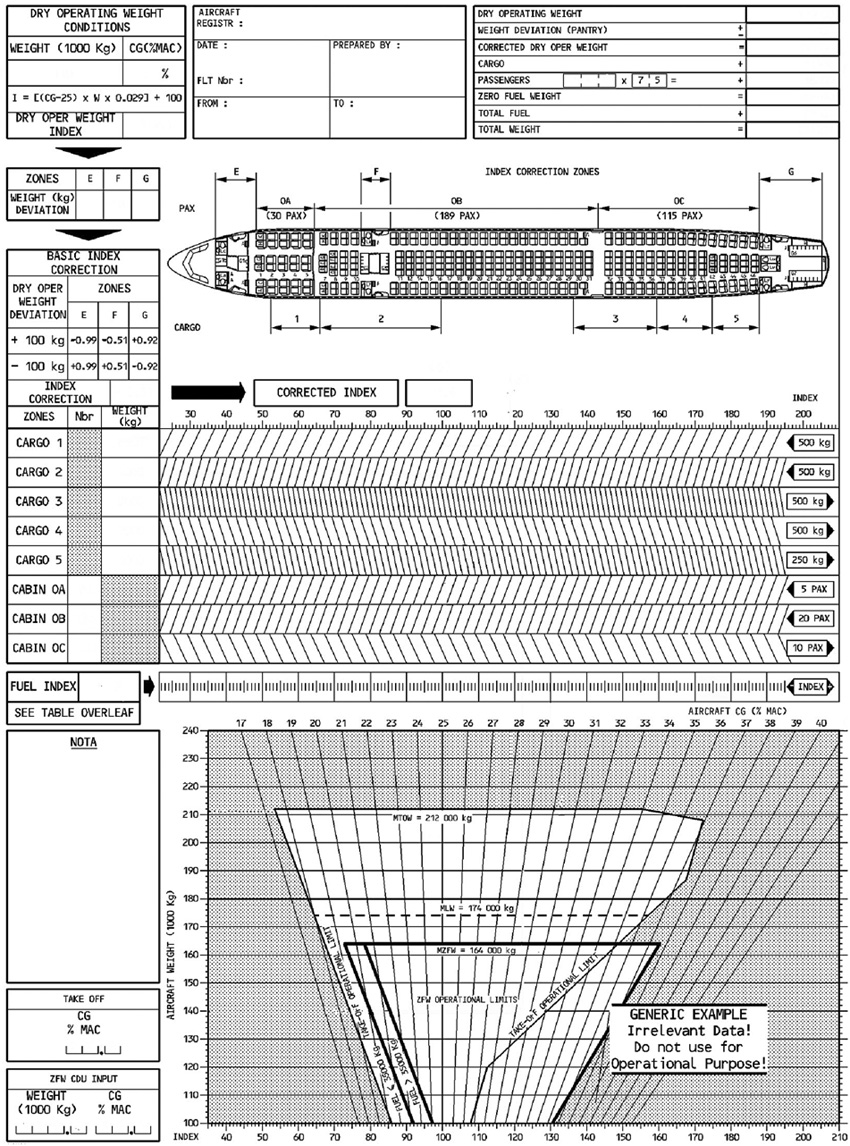
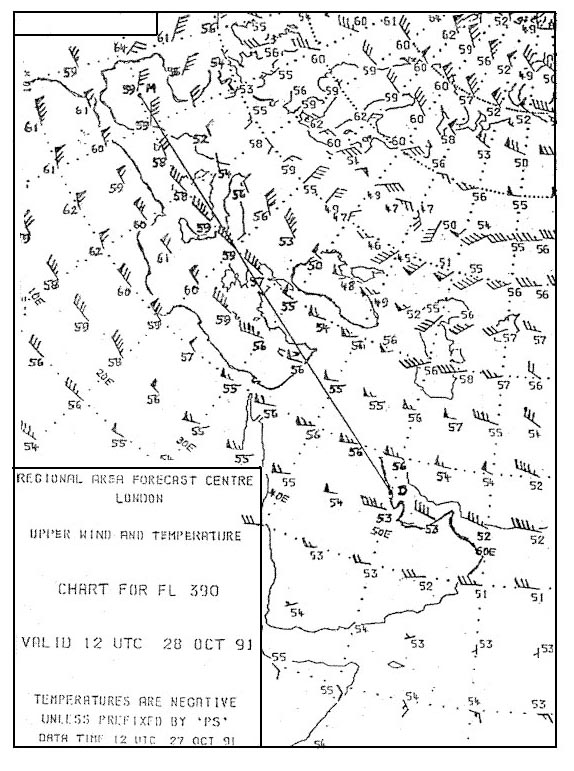
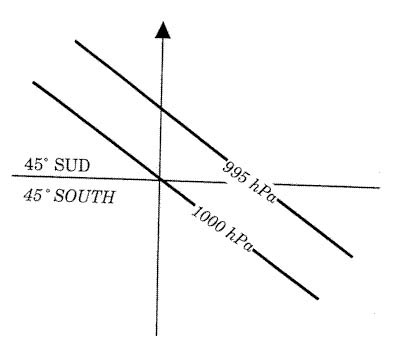
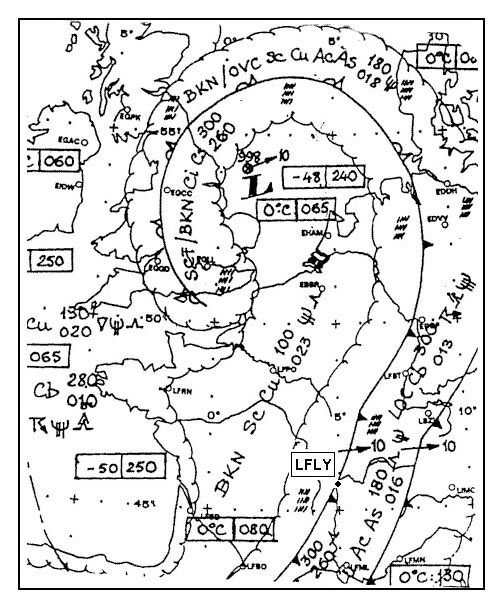
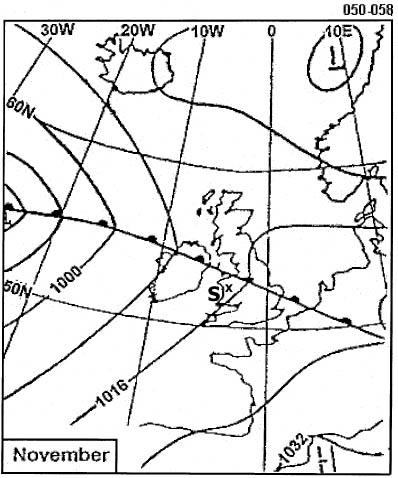
Sign up to unlock all our services and 15164 corrected and explained questions.
Question 145-1 : Which of the following statements concerning check list is correct ? [ Certification weather ]
Question 145-2 : Which of the following statements are correct with regard to the design of a check list.1 the longer a check list, the more it must be subdivided into logical parts.2 the trickiest points must be placed in the middle of the check list.3 check lists must be designed in such a way that they can be ?
1, 4 and 5 are correct.
Question 145-3 : According to rasmussen's model, errors in rule based control mode are of the following type s ?
Errors of technical knowledge.

Question 145-4 : According to rasmussen's model, errors are of the following type s in skill based behaviour ?
Question 145-5 : In order to overcome an overload of work during the flight, it is necessary to..1 know how to use one's own reserve of resources in order to ease the burden on the crew.2 divide up tasks among the crew.3 ensure that the long term memory is used as much as possible as short term memory will add to ?
1, 2 and 4 are correct.
Question 145-6 : The available cognitive resources of the human brain ?
Question 145-7 : The acquisition of a skill comprises three stages anderson model ?
Cognitive, associative and automatic.
Question 145-8 : A pilot can be described as being proficient, when he/she ?
Question 145-9 : With regard to the practice of english, which of the following statements is correct ?
Question 145-10 : What are the main consequences of latent errors they. 1 remain undetected in the system for a certain length of time.. 2 may only manifest themselves under certain conditions.. 3 are quickly detectable by the front line operator whose mental schemas on the instantaneous situation filter out formal ?
Question 145-11 : Pilot stress reactions ?
Question 145-12 : Which of the following provides the basis of all perceptions ?
Question 145-13 : The effect of experience and repetition on performance ?
Question 145-14 : Situations particularly vulnerable to 'reversion to an earlier behaviour pattern' are.1. when concentration on a particular task is relaxed.2. when situations are characterised by medium workload.3. when situations are characterised by stress ?
Question 145-15 : The most dangerous characteristic of perception is, that it ?
Question 145-17 : Which of the following are strategies for resolving conflict.1. seeking arbitration.2. actively listening to other people.3. abandoning facts so as to move the conversation to a more emotional level.4. becoming aware of cultural influences ?
Question 145-18 : What elements establish synergy within the crew ?
Question 145-19 : Which of the following statements best characterise a synergetic cockpit.1 decisions are taken by the captain, but prepared by the crew.2 there is little delegating of tasks.3 communications are few in number but precise and geared purely to the flight.4 fluid, consensual boundaries exist in ?
1, 4.
Question 145-20 : What may become the main risk of a laissez faire cockpit ?
Question 145-21 : What is characterized by a laissez faire cockpit ?
Question 145-22 : Which of the following operations are performed more effectively by people than by automatic systems.1. qualitative decision making.2. waiting for an infrequent phenomenon.3. monitoring to ensure that certain values are not exceeded.4. detections of of unusual conditions smell, noise, etc. ?
Question 145-23 : Which of the following operations are performed more effectively by automatic systems than by people.1. waiting for an infrequent phenomenon.2. long term controlling of a set value e.g holding of trajectory.3. monitoring to ensure that certain values are not exceeded e.g holding of flight path.4. ?
Question 145-24 : As a result of automation in cockpits ?
Question 145-25 : Which of the following drawbacks are associated with automation .1. reduced competence in manually controlling the aircraft.2. increased likelihood of slips while programming automatic systems.3. difficulties in adapting to the use of a sidestick.4. general decrease in technical reliability ?
Question 145-26 : What are main signs indicating the loss of vigilance.1. decrease in sensory perception.2. increase in selective attention.3. sensation of muscular heaviness.4. decrease in complacency.which of the following lists all the correct statements ?
Question 145-27 : Which of the following statements concerning hypovigilance is correct.hypovigilance ?
Question 145-28 : What are the main factors which bring about reduced or low vigilance hypovigilance.1. the monotony of the task.2. tiredness and the need for sleep.3. a lack of stimulation.4. excessive stress ?
Question 145-29 : Which of the following statements in regard to motivation is correct ?
Question 145-30 : Which of the following describes an autocratic cockpit ?
Question 145-31 : What distinguishes status from role ?
Question 145-32 : Which of the following elements make up the personality of an individual.1. heredity.2. childhood environment.3. upbringing.4. past experience ?
Question 145-33 : What is synergy in a crew ?
Question 145-34 : Which of the following statements concerning conflicts is correct ?
Question 145-35 : In terms of decision making, the intention to become integrated into the team, to be recognised as the leader or to avoid conflicts may lead to ?
The attempt to agree on decisions made by other crew members.
Question 145-36 : What strategy should be put in place when faced with an anticipated period of stress ?
Question 145-37 : Which biases relate to human decision making.1. personal experience tends to alter the perception of the risk of an event occurring.2. there is a natural tendency to want to confirm our decision even in the face of facts which contradict it.3. the group to which an individual belongs tends to ?
Question 145-38 : Decision making can be influenced by the following factors.1. people tend to conform to opinions expressed by a majority within the group they belong to.2. people always keep the future decisions in line with those their superiors have made in the past.3. people more easily tend to select data which ?
Question 145-39 : Decision making is a concept which represents ?
Question 145-40 : In problem solving, what determines the transition from rule based activities to a knowledge based activity ?
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5759 Free Training Exam