Which element of a position report may be omitted when ssr mode c information ? [ Assessment Aerodrome ]
Question 19-1 : The flight level or altitude the time the aircraft identification the position
 The flight level or altitude.
The flight level or altitude. A complete position report transmitted by radiotelephony shall contain the ?
Question 19-2 : 1 aircraft identification 2 position 3 time 4 flight level or altitude 5 next position and time over 6 ensuing significant point 1 aircraft identification 2 position 3 flight level or altitude 4 time 5 next position and time over 6 ensuing significant point 1 aircraft identification 2 position 3 time 4 true air speed 5 flight level or altitude 6 next position and time over 1 aircraft identification 2 position 3 time 4 flight level or altitude 5 next position 6 time over
 1) aircraft identification, 2) position, 3) time, 4) flight level or altitude, 5) next position and time over, 6) ensuing significant point.
1) aircraft identification, 2) position, 3) time, 4) flight level or altitude, 5) next position and time over, 6) ensuing significant point. The standard vertical separation minima between two aircraft flying in the same ?
Question 19-3 : 4000 feet 1000 feet 2500 feet 2000 feet
 4000 feet.
4000 feet. The 'mach number technique' may be applied by atc to aircraft along the same ?
Question 19-4 : Maintain longitudinal separation reduce the fuel burn in the cruise adjust the mach number as the aircraft`s mass reduces allow reduced vertical separation
 Maintain longitudinal separation.
Maintain longitudinal separation. The vectoring to intercept an ils localiser course or an mls final approach ?
Question 19-5 : 2 0 nm 3 0 nm 1 5 nm 2 5 nm
 2.0 nm.
2.0 nm. According to international agreements wind direction indications shall be ?
Question 19-6 : For take off and landing when the local variation exceeds 10 degrees for lower and upper wind forecasts when polewards of latitude 60 degrees in a pirep on request of a meteorological watch office mwo or at specified points
 For take-off and landing.
For take-off and landing. According to icao doc 4444 when an aircraft is radar vectored to an ils ?
Question 19-7 : 45 degrees 35 degrees 40 degrees 50 degrees
 45 degrees.
45 degrees. In advisory airspace class f airspace an air traffic advisory service may be ?
Question 19-8 : Ifr flights only controlled flights only vfr flights only all flights
 Ifr flights only.
Ifr flights only. In respect of the avoidance of collisions air traffic advisory services deliver ?
Question 19-9 : Advisory information mandatory avoidance instructions clearances tcas instructions
 Advisory information.
Advisory information. You are flying when you receive a broadcast from ats advising of the emergency ?
Question 19-10 : Continue according to current atc clearance change to the previous frequency and request instructions clear the area and stand by on the appropriate frequency transmit on the frequency your call sign position track and level
 Continue according to current atc clearance
Continue according to current atc clearance What is the code word used in air traffic incident reports to designate ?
Question 19-11 : Airprox acprox airdist proximity
 Airprox
Airprox What is the meaning of the code word 'airprox' ?
Question 19-12 : Aircraft proximity air professional report airman pressure oxygen airborne processed oxygen
 Aircraft proximity
Aircraft proximity Which of the following occurrences should be reported in an air traffic ?
Question 19-13 : Faulty procedures leading to an airprox unruly passengers on board rostering leading to flight crew duty time exceedances aircraft mechanical failures
 Faulty procedures leading to an airprox.
Faulty procedures leading to an airprox. According to icao pans atm air traffic management what is the definition for ?
Question 19-14 : The point to which an aircraft is granted an air traffic control clearance a broadcast from an air traffic services unit that limits the use of a specific airspace the last portion of an air traffic control clearance the point at which the aircraft reaches the initial approach fix
 The point to which an aircraft is granted an air traffic control clearance.
The point to which an aircraft is granted an air traffic control clearance. An aircraft is in the descent and has been receiving instructions from atc to ?
Question 19-15 : 4 nm 6 nm 5 nm 8 nm
 4 nm
4 nm General provisions – change from ifr to vfr – a change from ifr to vfr is ?
Question 19-16 : The change is initiated by the pic with a message containing the specific expression cancel ifr flight atc invites the pic to change from ifr to vfr the pic has requested and obtained an atc clearance for the change and has filed an ats flight plan for a special vfr flight the position of the change has been noted on the atc flight plan the cancellation of the flight under ifr will then be made automatically by atc
 The change is initiated by the pic with a message containing the specific expression “cancel ifr flight”.
The change is initiated by the pic with a message containing the specific expression “cancel ifr flight”. The wake turbulence category light groups aircraft types with a maximum ?
Question 19-17 : 7000 kg or less 5700 kg or less 8168 kg or less 15 000 kg or less
 7000 kg or less.
7000 kg or less. Area control centres issue clearances for the purpose of ?
Question 19-18 : Achieving separation between controlled flights providing flight information service achieving separation between ifr flights providing advisory service
 Achieving separation between controlled flights
Achieving separation between controlled flights On approach to landing the wind is reported 040/20 kt which runways below is ?
Question 19-19 : 06 09 27 36
 06
06 You are flying above bristol and need to dump the fuel what do you need to do ?
Question 19-20 : Climb to 6000 ft and fly over bristol channel then dump the fuel climb to 4000 ft and dump fuel climb to 5000 ft and fly over bristol channel then dump the fuel climb to 3000 ft and dump fuel
 Climb to 6000 ft and fly over bristol channel, then dump the fuel.
Climb to 6000 ft and fly over bristol channel, then dump the fuel. A pilot should report 'runway vacated' ?
Question 19-21 : When the entire aircraft has passed the relevant holding point when the aircraft is turning to exit the runway when the entire aircraft has vacated the runway as soon as the aircraft nose is beyond the limits of the runway
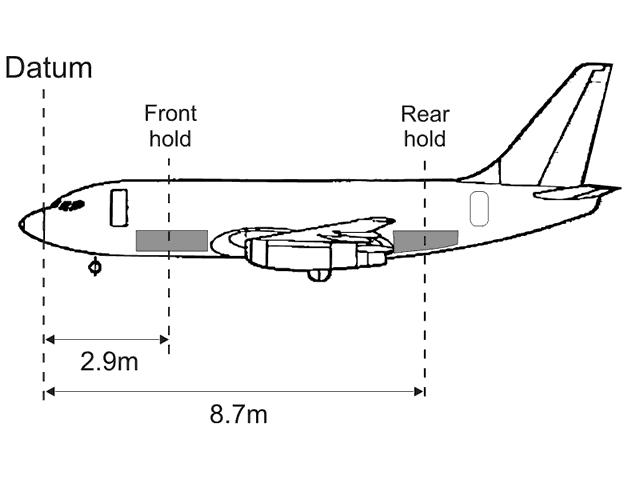 When the entire aircraft has passed the relevant holding point.
When the entire aircraft has passed the relevant holding point. A flight from new york jfk is preparing for taxi given the following ?
Question 19-22 : Make a request for runway 31l for safety reasons delay until wind changes wait until atc changes runways from 31r to 31l offload one container of cargo so that the aircraft is able to take off from runway 31r
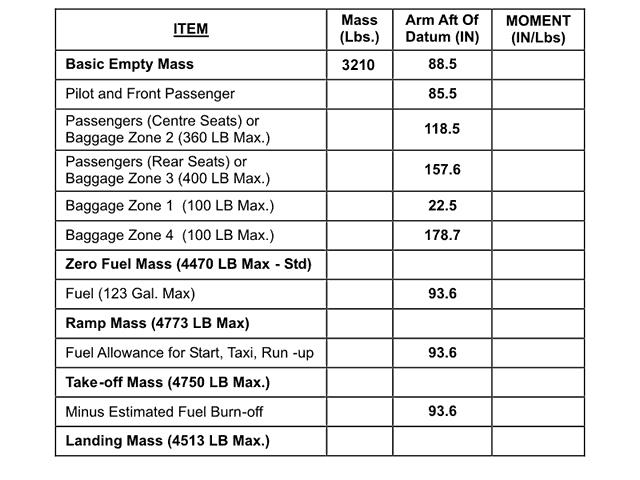 Make a request for runway 31l for safety reasons.
Make a request for runway 31l for safety reasons. Which word should be used to indicate an aircraft of 136 000 kg ?
Question 19-23 : Heavy light medium super heavy
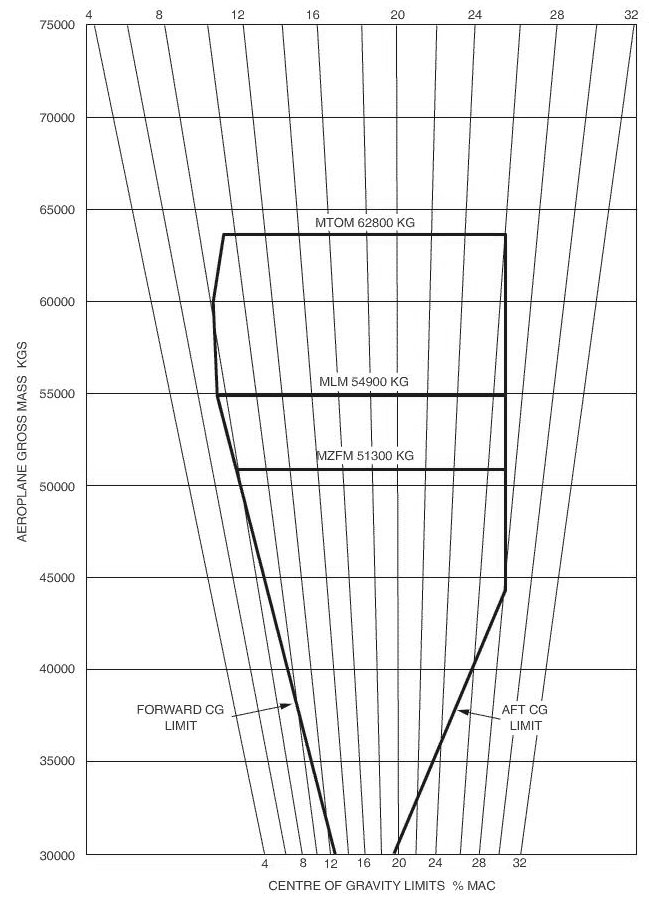 Heavy
Heavy A light aircraft is an aircraft which weighs a maximum of… ?
Question 19-24 : 7000 kg 7600 kg 6800 kg 7700 kg
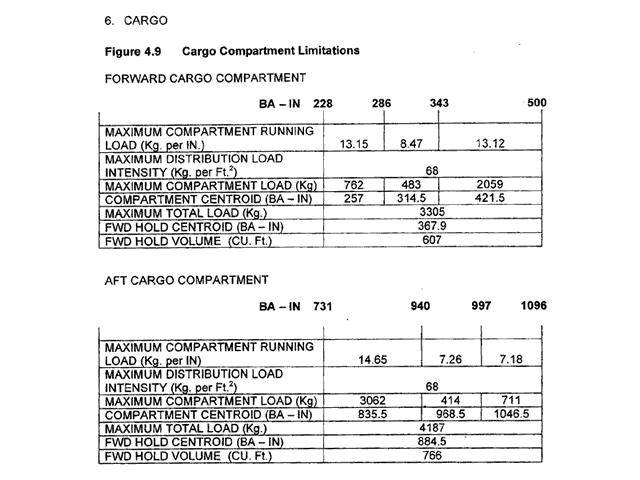 7000 kg
7000 kg For independent parallel approaches when vectoring to intercept the ils ?
Question 19-25 : 30 45 20 15
 30
30 Select the option which correctly states in the increasing order of seriousness ?
Question 19-26 : Incerfa alerfa detresfa incerfa alerfa distresfa alerfa incerfa detresfa alerfa distresfa rescuefa
 Incerfa, alerfa, detresfa.
Incerfa, alerfa, detresfa. 'milano approach bigjet 337 heavy over undap' the aircraft’s correct callsign ?
Question 19-27 : Bigjet 337 milano approach bigjet bigjet 337 heavy
 Bigjet 337
Bigjet 337 A clearance is received which items must be read back to atc 1 wind speed and ?
Question 19-28 : 3 4 5 6 and 7 1 2 3 6 and 7 2 3 4 5 and 6 1 3 4 6 and 7
 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7.
3, 4, 5, 6 and 7. If no information has been received what information is given to an aircraft on ?
Question 19-29 : Runway in use wind qnh and visibility below 10 km runway in use wind qnh visibility below 10 km transition level and time runway in use qnh and visibility below 10 km runway in use wind qnh and transition level
 Runway in use, wind, qnh and visibility below 10 km.
Runway in use, wind, qnh and visibility below 10 km. According to icao annex 11 the lateral limits of a control zone shall extend to ?
Question 19-30 : 5 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned 3 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned 4 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned 10 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned
 5 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned
5 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned The french safety board bea published a preliminary report of a serious ?
Question 19-31 : They had to reduce the aircraft's mass in order to safely land below the maximum landing mass they made a mistake according to normal procedures the aircraft should have landed with all the remaining usable fuel they had to mitigate against the risk of fire and therefore empty the fuel tanks as much as possible after take off it is a normal procedure to dump some fuel in order to reduce pollution
 They had to reduce the aircraft's mass in order to safely land below the maximum landing mass.
They had to reduce the aircraft's mass in order to safely land below the maximum landing mass. According to icao doc 4444 pans atm what word s shall be included immediately ?
Question 19-32 : Heavy super heavy medium large
According to sera standardised european rules of the air when an ifr pilot ?
Question 19-33 : Notify atc however if the weather conditions are imc during the flight the flight must remain under ifr notify atc however if the weather conditions are vmc during the flight the flight must remain under ifr request an atc approval a change from ifr to vfr does not depend on weather conditions request an atc approval the flight should then be performed above 3000 ft amsl
 Notify atc. however, if the weather conditions are imc during the flight, the flight must remain under ifr.
Notify atc. however, if the weather conditions are imc during the flight, the flight must remain under ifr. According to icao annex 11 to whom may the task of providing services on the ?
Question 19-34 : An aerodrome control tower an approach control unit a flight information unit an area control centre
 An aerodrome control tower.
An aerodrome control tower. Consider the following forms of position information passed on to an aircraft ?
Question 19-35 : 1 2 and 4 1 and 5 2 and 4 1 3 and 5
 1, 2 and 4.
1, 2 and 4. An aircraft arriving at paris cdg receives the following atis . . 'this is cdg ?
Question 19-36 : Correct incorrect because the type of approach is mentioned incorrect because the snowtam is missing incorrect because the rvrs are not mentioned
 Correct.
Correct. Why is fuel dumped during an emergency after take off ?
Question 19-37 : To get below maximum landing mass mlm lower risk of fire during landing to not damage the runway while landing to have a better airplane manoeuvrability and get back to the airport quickly for landing
 To get below maximum landing mass (mlm).
To get below maximum landing mass (mlm). Which option is correct as regards to air traffic services or air traffic ?
Question 19-38 : Advisory services do not deliver clearances but only advisory information and can use the word suggest advisory services deliver clearances and advisory information and do not use the word suggest control services deliver advisories and suggestions and do not use the word cleared' control services do not deliver clearances but only hearing information and use the phrases can i or do you allow me
 Advisory services do not deliver “clearances” but only “advisory information” and can use the word “suggest”....
Advisory services do not deliver “clearances” but only “advisory information” and can use the word “suggest”.... According to icao doc 4444 why must the movement of all persons vehicles and ?
Question 19-39 : To reduce hazards between aircraft landing taxiing or taking off to ensure that emergency vehicles are given priority to avoid damage to aerodrome navigation aids to provide safe vehicular access to aprons
 To reduce hazards between aircraft landing, taxiing, or taking off.
To reduce hazards between aircraft landing, taxiing, or taking off. What conditions does sera allow aeroplanes to take off and land in a direction ?
Question 19-40 : Wherever safety air traffic considerations or runway configurations dictate it only for the interest of safety only when an air traffic controller requires it or authorizes it whenever the pilot in command informs air traffic control that they intend to do so
 Wherever safety, air traffic considerations or runway configurations dictate it.
Wherever safety, air traffic considerations or runway configurations dictate it. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
719 Free Training Exam Other source study: Furious atpl examen 19
