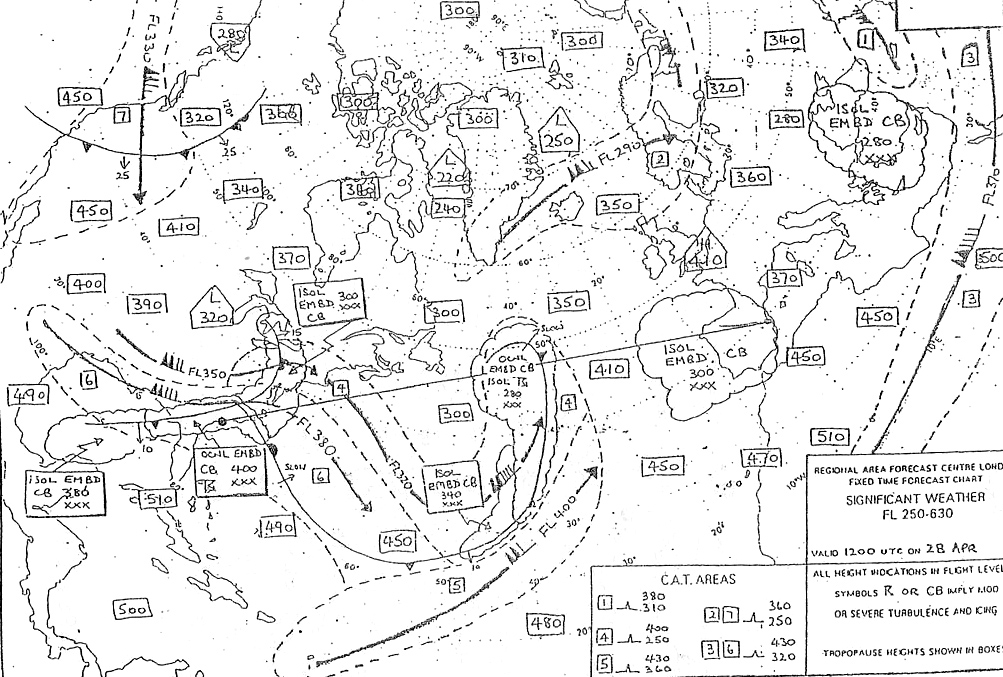
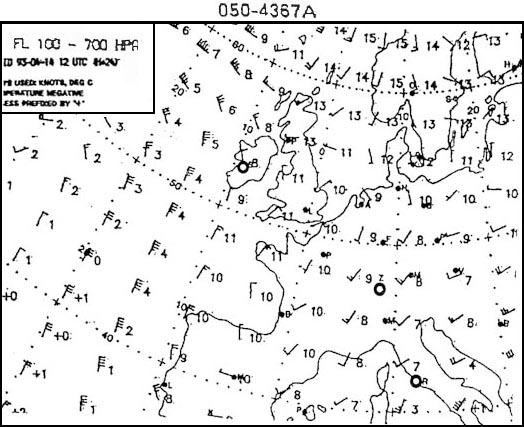
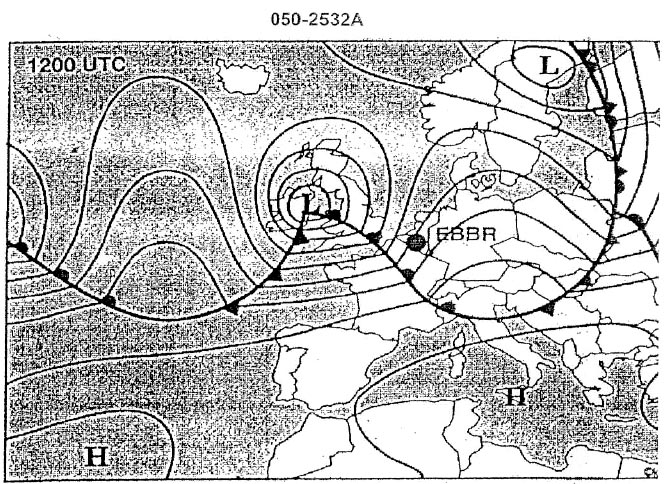
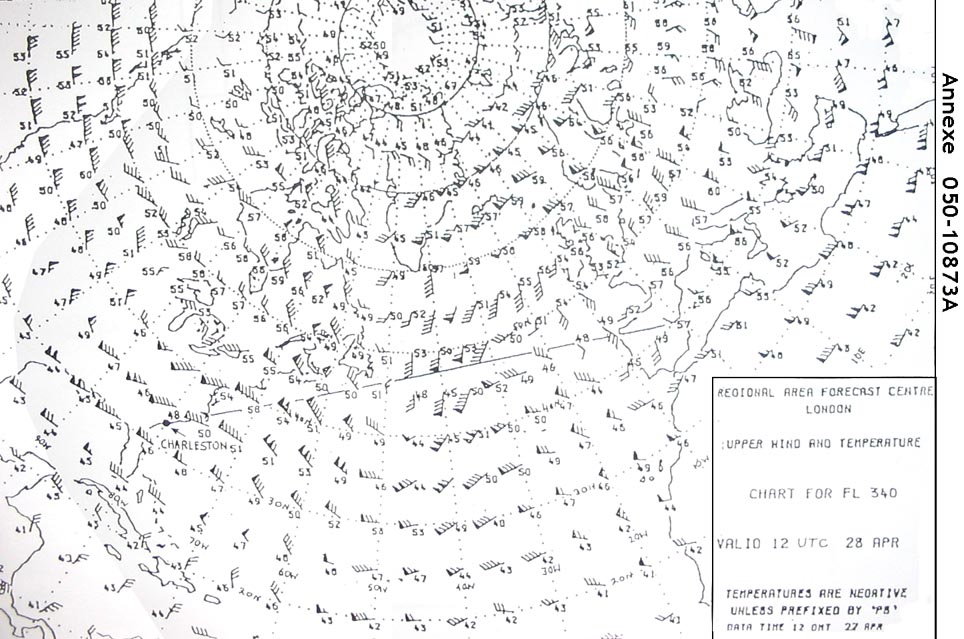
Sign up to unlock all our services and 15164 corrected and explained questions.
Question 199-1 : Given.gs = 120 kt. distance from a to b = 84 nm..what is the time from a to b ? [ Level reports ]
Question 199-2 : Given.distance 'a' to 'b' 1973 nm.ground speed out 430 kt.ground speed back 385 kt.safe endurance 7 hr 20 min.the distance from 'a' to the point of safe return psr is ?
1490 nm.

Question 199-3 : Given.distance 'a' to 'b' 2346 nm.ground speed out 365 kt.ground speed back 480 kt.the time from 'a' to the point of equal time pet between 'a' and 'b' is ?
Question 199-4 : Given.distance 'q' to 'r' 1760 nm.ground speed out 435 kt.ground speed back 385 kt.the time from 'q' to the point of equal time pet between 'q' and 'r' is ?
Question 199-5 : Given.distance 'q' to 'r' 1760 nm.ground speed out 435 kt.ground speed back 385 kt.safe endurance 9 hr.the distance from 'q' to the point of safe return psr between 'q' and 'r' is ?
1838 nm.
Question 199-6 : An aeroplane is flying at tas 180 kt on a track of 090°..the w/v is 045° / 50kt..how far can the aeroplane fly out from its base and return in one hour ?
85 nm.
Question 199-7 : An aircraft is maintaining a 5.2% gradient is at 7 nm from the runway, on a flat terrain, its height is approximately ?
Question 199-8 : An aircraft descends from fl250 to fl100..the rate of descent is 1000 ft/min, the gs is 360 kt..the flight path angle is ?
Question 199-9 : The outer marker of an ils with a 3° glide slope is located 4.6 nm from the threshold. assuming a glide slope height of 50 ft above the threshold, the approximate height of an aircraft passing the outer marker is ?
1450 ft.
Question 199-11 : How long will it take to fly 5 nm at a groundspeed of 269 kt ?
Question 199-12 : An aircraft travels 2.4 statute miles in 47 seconds. what is its groundspeed ?
Question 199-14 : Assuming zero wind, what distance will be covered by an aircraft descending 15000 ft with a tas of 320 kt and maintaining a rate of descent of 3000 ft/min ?
Question 199-15 : An island appears 30° to the left of the centre line on an airborne weather radar display. what is the true bearing of the aircraft from the island if at the time of observation the aircraft was on a magnetic heading of 276° with the magnetic variation 12°w ?
Question 199-16 : An aircraft at fl370 is required to commence descent at 120 nm from a vor and to cross the facility at fl130. if the mean gs for the descent is 288 kt, the minimum rate of descent required is ?
Question 199-17 : An aircraft at fl310, m0.83, temperature 30°c, is required to reduce speed in order to cross a reporting point five minutes later than planned. assuming that a zero wind component remains unchanged, when 360 nm from the reporting point mach number should be reduced to ?
M0.74
Question 199-18 : A ground feature was observed on a relative bearing of 325° and five minutes later on a relative bearing of 280°. the aircraft heading was 165° m , variation 25°w, drift 10°right and gs 360 kt..when the relative bearing was 280°, the distance and true bearing of the aircraft from the feature was ?
30 nm and 240°.
Question 199-19 : An aircraft at fl350 is required to descend to cross a dme facility at fl80. maximum rate of descent is 1800 ft/min and mean gs for descent is 276 kt. the minimum range from the dme at which descent should start is ?
Question 199-20 : An aircraft at fl120, ias 200kt, oat 5° and wind component +30kt, is required to reduce speed in order to cross a reporting point 5 min later than planned..assuming flight conditions do not change, when 100 nm from the reporting point ias should be reduced to ?
Question 199-21 : An aircraft at fl350 is required to cross a vor/dme facility at fl110 and to commence descent when 100 nm from the facility. if the mean gs for the descent is 335 kt, the minimum rate of descent required is ?
Question 199-22 : An aircraft at fl370, m0.86, oat 44°c, headwind component 110 kt, is required to reduce speed in order to cross a reporting point 5 minutes later than planned. if the speed reduction were to be made 420 nm from the reporting point, what mach number is required ?
Question 199-23 : An aircraft at fl390 is required to descend to cross a dme facility at fl70. maximum rate of descent is 2500 ft/min, mean gs during descent is 248 kt. what is the minimum range from the dme at which descent should commence ?
Question 199-24 : An aircraft at fl370 is required to commence descent when 100 nm from a dme facility and to cross the station at fl120..if the mean gs during the descent is 396 kt, the minimum rate of descent required is approximately ?
Question 199-25 : An aircraft at fl140, ias 210 kt, oat 5°c and wind component minus 35 kt, is required to reduce speed in order to cross a reporting point 5 minutes later than planned. assuming that flight conditions do not change, when 150 nm from the reporting point the aircraft should reduce ias by ?
20 kt.
Question 199-26 : At 0422 an aircraft at fl370, gs 320kt, is on the direct track to vor 'x' 185 nm distant..the aircraft is required to cross vor 'x' at fl80..for a mean rate of descent of 1800 ft/min at a mean gs of 232 kt, the latest time at which to commence descent is ?
04h45.
Question 199-27 : An aircraft at fl330 is required to commence descent when 65 nm from a vor and to cross the vor at fl100. the mean gs during the descent is 330 kt. what is the minimum rate of descent required ?
Question 199-28 : An aircraft at fl290 is required to commence descent when 50 nm from a vor and to cross that vor at fl80. mean ground speed during descent is 271kt. what is the minimum rate of descent required ?
Question 199-29 : An aircraft at fl350 is required to commence descent when 85 nm from a vor and to cross the vor at fl80. the mean gs for the descent is 340 kt. what is the minimum rate of descent required ?
Question 199-30 : An aircraft is planned to fly from position 'a' to position 'b', distance 480 nm at an average ground speed of 240 kt. it departs 'a' at 1000 utc. after flying 150 nm along track from 'a', the aircraft is 2 minutes behind planned time..using the actual gs experienced, what is the revised eta at 'b' ?
Question 199-31 : An aircraft is planned to fly from position 'a' to position 'b',distance 320 nm, at an average gs of 180 kt. it departs 'a' at 1200 utc. after flying 70 nm along track from 'a', the aircraft is 3 minutes ahead of planned time..using the actual gs experienced, what is the revised eta at 'b' ?
Question 199-32 : An aircraft is planned to fly from position 'a' to position 'b', distance 250 nm at an average gs of 115 kt. it departs 'a' at 0900 utc. after flying 75 nm along track from 'a', the aircraft is 1.5 minute behind planned time..using the actual gs experienced, what is the revised eta at 'b' ?
11 15 utc.
Question 199-33 : Given.distance 'a' to 'b' is 475 nm, planned gs 315 kt, atd actual time departure 1000 utc..at 1040 utc a fix is obtained at 190 nm along track..what gs must be maintained from the fix in order to achieve planned eta at 'b' ?
Question 199-34 : Given distance 'a' to 'b' is 325 nm, planned gs 315 kt, atd 1130 utc, 1205 utc fix obtained 165 nm along track..what gs must be maintained from the fix in order to achieve planned eta at 'b' ?
Question 199-35 : Given distance a to b is 100 nm, fix obtained 40 nm along and 6 nm to the left of course. what heading alteration must be made to reach 'b' ?
Question 199-36 : Given distance 'a' to 'b' is 90 nm, fix obtained 60 nm along and 4 nm to the right of course..what heading alteration must be made to reach 'b' ?
Question 199-37 : Complete line 1 of the 'flight navigation log'.positions 'a' to 'b'. what is the hdg° m and eta. 2497 ?
Question 199-38 : Complete line 2 of the 'flight navigation log', positions 'c' to 'd'. what is the hdg° m and eta. 2497 ?
Question 199-39 : Complete line 3 of the 'flight navigation log', positions 'e' to 'f'. what is the hdg° m and eta. 2497 ?
Question 199-40 : Complete line 4 of the 'flight navigation log', positions 'g' to 'h'. what is the hdg° m and eta. 2497 ?
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
7919 Free Training Exam