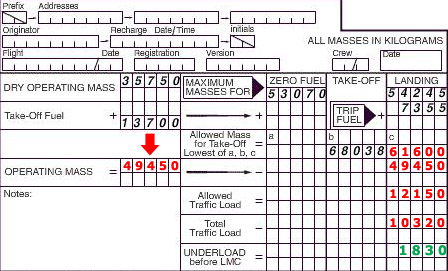
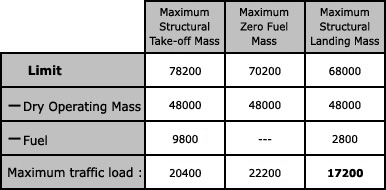
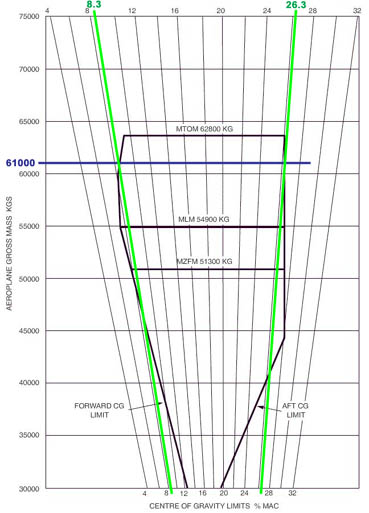
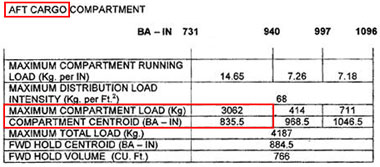
A pilot is on the approach into an aerodrome in an aircraft in the medium wake ? [ Admission airport ]
Question 20-1 : 5 0 nm 3 0 nm 4 0 nm 6 0 nm
 5.0 nm
5.0 nm A runway in use for landing operations has been selected for noise abatement ?
Question 20-2 : Be refused by the pilot in command for safety reasons no longer be used when the ceiling lowers to 2500 ft no longer be used when the visibility decreases to 2500 m still be selected for this purpose with a localiser only approach
 Be refused by the pilot-in-command for safety reasons.
Be refused by the pilot-in-command for safety reasons. A pilot is in contact with berlin atc suddenly the aeroplane depressurises and ?
Question 20-3 : Contact berlin atc or switch to 121 5 mhz frequency request the atc unit which frequency he/she should contact to declare an emergency contact eurocontrol and if unsuccessful revert to berlin atc immediately switch to 121 5 mhz frequency and wait for clearance to deliver the message
 Contact berlin atc or switch to 121.5 mhz frequency.
Contact berlin atc or switch to 121.5 mhz frequency. After vacating the active runway and while taxiing towards the apron the tower ?
Question 20-4 : 1 and 2 2 and 3 3 and 4 4 and 5
 1 and 2
1 and 2 An airbus a380 performs a visual approach at rome fiumicino the aircraft is ?
Question 20-5 : Atc is no longer required to apply wake turbulence separation between the a320 and the a380 atc must inform the a320 about the wake turbulence category of the a380 the pilot of the a320 must maintain the wake turbulence separation from the a380 atc is responsible for separating the a380 from the a320 by applying the appropriate wake turbulence separation minima
 Atc is no longer required to apply wake turbulence separation between the a320 and the a380.
Atc is no longer required to apply wake turbulence separation between the a320 and the a380. Atc realises that they are unable to maintain adequate horizontal separation ?
Question 20-6 : Atc should vector such aircraft to different flight levels to provide vertical separation atc should advise the flight crew to establish and maintain visual seperation atc should ask the flight crew with tcas capabilities to rely on the tcas and to maintain their own separation atc should allow a reduction in the horizontal separation to half of the prescribed minima
 Atc should vector such aircraft to different flight levels to provide vertical separation.
Atc should vector such aircraft to different flight levels to provide vertical separation. An aircraft is in receipt of atis broadcast 'otopeni information oscar' this ?
Question 20-7 : Type of approach s to be expected the runway s in use present weather standard arrival route s to be expected the runway s in use aerodrome altitude departure route s to be expected the runway s in use aerodrome altitude taxi out delay runway s physical characteristics present weather
 Type of approach(s) to be expected, the runway(s) in use, present weather.
Type of approach(s) to be expected, the runway(s) in use, present weather. Regarding the clearance message . speedjet 645 cleared to athens via the ?
Question 20-8 : Wind destination flight level squawk
 Wind
Wind Both an aeroplane call sign ab139 and a helicopter call sign at139 are ?
Question 20-9 : Request a temporary change in one of the two call signs make use of the abbreviated call signs for the helicopter and the aeroplane instruct both the aeroplane and the helicopter to change their call signs permanently continue using the existing call signs and exercise caution to avoid confusion
 Request a temporary change in one of the two call signs.
Request a temporary change in one of the two call signs. An aircraft is cruising at fl130 atc issues a climb clearance to fl150 this new ?
Question 20-10 : Unable refused cannot impossible
 Unable.
Unable. Atc is providing radar control to a flight operating under ifr instrument ?
Question 20-11 : The pilot and atc the pilot only atc only the operator and atc
 The pilot and atc.
The pilot and atc. What do atc provide to an aircraft during radar vectoring ?
Question 20-12 : Headings to fly tracks to fly vor radials to intercept ssr codes
 Headings to fly.
Headings to fly. Two aircraft are flying at the same level one on radial 010° outbound and ?
Question 20-13 : A vor an ndb a tacan a dme
 A vor.
A vor. Atc have access to both psr and ssr primary and secondary surveillance radar ?
Question 20-14 : 1 2 and 4 2 3 and 4 1 3 and 5 1 2 and 5
 1, 2 and 4
1, 2 and 4 According to icao doc 4444 describe what actions a pilot shall make after ?
Question 20-15 : Continue according to current clearance and maintain a listening watch on the frequency in use for any further instructions from the ats unit and watch for conflicting traffic both visually and by reference to acas if equipped navigate as deemed appropriate by the pilot and acknowledge to the appropriate ats unit that the notification about the emergency descent was received immediately acknowledge the receipt of the broadcast and request further instructions navigate as deemed appropriate by the pilot and turn on all aircraft exterior lights commensurate with appropriate operating limitations
 Continue according to current clearance and maintain a listening watch on the frequency in use for any further instructions from the ats unit, and watch for conflicting traffic both visually and by reference to acas (if equipped).
Continue according to current clearance and maintain a listening watch on the frequency in use for any further instructions from the ats unit, and watch for conflicting traffic both visually and by reference to acas (if equipped). The tower has issued a landing clearence to an aircraft on short final who ?
Question 20-16 : Advise area controller after 5 min sound the crash alarm and inform rescue services after 20 min advise area controller after 20 min sound the crash alarm and inform rescue services after 5 min
An aircraft is on final approach to land on rwy 04 in stansted in order to ?
Question 20-17 : 1 4 nm 2 20 kt 1 4 km 2 20 km/h 1 7 nm 2 20 kt 1 7 nm 2 40 kt
 (1) 4 nm; (2) 20 kt
(1) 4 nm; (2) 20 kt A runway inspection shows that there is standing water on the runway this ?
Question 20-18 : Provide the necessary information to arriving and departing aircraft calculate the runway pavement classification number and update aerodrome charts provide the necessary information to departing aircraft only provide the necessary information to arriving aircraft only
A heavy aircraft is landing behind a light aircraft atc asks the heavy aircraft ?
Question 20-19 : To get a safe order flow of traffic the pilot shall not receive a landing clearance and will be expected to land after the preceding aircraft vacates the runway to assure wake turbulence separation the pilot must not delay the approach and must maintain high speed until at least 4 nm to touchdown
 To get a safe order flow of traffic.
To get a safe order flow of traffic. What should be advised by atc to the pilot prior to taxi if no information has ?
Question 20-20 : 1 2 3 5 6 and 8 1 2 3 4 5 and 6 1 3 4 5 6 and 8 2 3 4 6 7 and 8
 1, 2, 3, 5, 6 and 8.
1, 2, 3, 5, 6 and 8. The approach control unit is providing services to departing aircraft when it ?
Question 20-21 : Without delay to departing aircraft to already departed aircraft above the transition level if the unit determines that this is significant if requested to provide a weather update by a pilot
 Without delay to departing aircraft.
Without delay to departing aircraft. An aircraft is flying towards a major aerodrome and is part of a traffic flow ?
Question 20-22 : Be correct for an approach sequence at the destination have a vertical separation of 1000 ft when operating within rvsm airspace be separated by at least 500 ft depending on traffic levels have a vertical separation of 1000 ft when operating below rvsm airspace
 Be correct for an approach sequence at the destination.
Be correct for an approach sequence at the destination. While in vmc a b737 is established on an rnp apch atc instructs the b737 pilot ?
Question 20-23 : Must ensure that the spacing from the preceding aircraft is acceptable for wake turbulence purposes shall not receive a landing clearance and he/she will be expected to land after the preceding aircraft vacates the runway must reduce speed to ensure maximum spacing from the preceding aircraft for wake turbulence purposes must not delay the approach and must maintain high speed until at least 4 nm to touchdown
 Must ensure that the spacing from the preceding aircraft is acceptable for wake turbulence purposes.
Must ensure that the spacing from the preceding aircraft is acceptable for wake turbulence purposes. The local qnh is 1018 6 hpa the pilots shall receive it as… ?
Question 20-24 : 1018 hpa 1020 hpa 1019 hpa 1010 hpa
 1018 hpa
1018 hpa An aircraft is being radar vectored what instructions will the controller give ?
Question 20-25 : Resume own navigation fly direct to 'lesda' magnetic track 150 distance to 'lesda' 41 nautical miles radar service terminated fly direct to 'lesda' proceed with own navigation resume previous navigation position 15 nm south of vor xy
 Resume own navigation. fly direct to 'lesda', magnetic track 150, distance to 'lesda' 41 nautical miles.
Resume own navigation. fly direct to 'lesda', magnetic track 150, distance to 'lesda' 41 nautical miles. An aerodrome meteorologist measures the qnh as 1006 6 hpa what qnh value will ?
Question 20-26 : 1006 hpa 1007 hpa 1005 hpa 1010 hpa
 1006 hpa
1006 hpa Before take off a pilot receives the following departure clearance 'climb via ?
Question 20-27 : Has to climb to fl100 comply with published level restriction follow the lateral profile of the sid and comply with published speed restrictions or atc issued speed control instructions may climb to fl100 must to comply with published level restriction can deviate from the lateral profile of the sid and must comply with published speed restrictions or atc issued speed control instructions has to climb to fl100 may deviate from published level restriction must follow the lateral profile of the sid and comply with published speed restrictions or atc issued speed control instructions are cleared to climb to fl100 may comply with published level restriction follow the lateral profile of the sid and may follow published speed restrictions or atc issued speed control instructions
 Has to climb to fl100, comply with published level restriction, follow the lateral profile of the sid, and comply with published speed restrictions or atc issued speed control instructions.
Has to climb to fl100, comply with published level restriction, follow the lateral profile of the sid, and comply with published speed restrictions or atc issued speed control instructions. An atis is broadcast… ?
Question 20-28 : For arriving and departing aircraft preferably on a vor frequency for departing and arriving aircraft lasting one minute in english only for departing aircraft on the ils localiser frequency for arriving aircraft on the ils localiser frequency
 For arriving and departing aircraft, preferably on a vor frequency.
For arriving and departing aircraft, preferably on a vor frequency. The crew of a boeing 747 on a transoceanic flight have been assigned a speed of ?
Question 20-29 : They must contact atc to notify them of the change as soon as possible reduce mach number without contacting atc they can reduce their speed immediately as the traffic behind will also have to reduce speed due to turbulence they can change their mach number by up to m0 05 without notifying atc
 They must contact atc to notify them of the change as soon as possible.
They must contact atc to notify them of the change as soon as possible. Who is in charge of traffic separation during a vfr approach ?
Question 20-30 : The pilot in command atc atc and the pilot in command nobody
 The pilot in command
The pilot in command Sometimes a single flight information region fir is delineated to include upper ?
Question 20-31 : To limit the amount of firs a high flying aircraft must operate in to limit the amount of firs a low flying aircraft must operate in to limit the amount of vhf frequency changes for low flying aircraft to limit the amount of vlf frequency changes for high flying aircraft
 To limit the amount of firs a high-flying aircraft must operate in.
To limit the amount of firs a high-flying aircraft must operate in. After landing when should the pilot report 'runway vacated' ?
Question 20-32 : When the entire aircraft is beyond the runway holding position when the aircraft starts turning to take the exit taxiway as soon as the aircraft is on the exit taxiway and at taxi speed as soon as the aircraft has crossed the runway edge line
 When the entire aircraft is beyond the runway-holding position.
When the entire aircraft is beyond the runway-holding position. Under what circumstances can separation minima be reduced between two aircraft ?
Question 20-33 : 1 and 3 only 1 2 and 4 1 and 2
 1 and 3
1 and 3 The 'mach number technique' may be applied by atc to aircraft along the same ?
Question 20-34 : Organize safety and an orderly traffic flow reduce vertical separation make the cruise flight more efficient reduce fuel burn
 Organize safety and an orderly traffic flow.
Organize safety and an orderly traffic flow. If there is a change in the active runway will an atis containing arrival and ?
Question 20-35 : Yes immediately no the changes will be transmitted to arriving aircraft by atc with the next regular report within 15 minutes from the change
 Yes, immediately.
Yes, immediately. The pilots have received clearance to taxi to the holding point of runway 27 ?
Question 20-36 : Take off rwy 27 or request rwy 04 and wait take off rwy 27 and file a incident report request rwy 04 which will be granted immediately request rwy 04 and file a incident report
 Take-off rwy 27 or request rwy 04 and wait.
Take-off rwy 27 or request rwy 04 and wait. What are the different types of horizontal separation ?
Question 20-37 : Time nm time speed dme distance dme distance speed time speed
 Time, nm.
Time, nm. After receiving initial information before taxiing the pilot of an aircraft ?
Question 20-38 : 1 2 6 and 8 1 3 and 4 1 2 3 4 and 7 1 2 3 4 6 and 8
 1, 2, 6 and 8.
1, 2, 6 and 8. What are the methods of lateral separation between aircraft according to icao ?
Question 20-39 : 1 2 and 3 2 and 3 2 and 4 1 2 and 4
 1, 2 and 3
1, 2 and 3 Select the service provided by ats unit at b taking into account the following ?
Question 20-40 : Air traffic advisory service with reduced safety compared to unit a air traffic control service with the same degree of safety as unit a air traffic control service with increased safety compared to unit a alerting service with reduced safety compared to unit a
 Air traffic advisory service, with reduced safety compared to unit a.
Air traffic advisory service, with reduced safety compared to unit a. Organize.
This page gathers the questions that you have marked as requiring additional review by clicking on the Review button under the questions of your choice. You can also add a personal annotation to each question to better organize your revisions. This tool helps you better target the concepts to be deepened and to progress effectively.
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
759 Free Training Exam Other source study: Furious atpl examen 20
