Longitudinal stability is directly influenced by ? [ Formation assignment ]
Question 230-1 : Centre of gravity position wing dihedral the vertical stabiliser elevator deflection only
 Centre of gravity position.
Centre of gravity position. An aeroplane with a cg location behind the centre of pressure of the wing can ?
Question 230-2 : Upwards zero downwards upwards or downwards depending on elevator deflection
 Upwards.
Upwards. In a skidding turn the nose pointing inwards compared with a co ordinated turn ?
Question 230-3 : I too small ii displaced towards the high wing i too large ii displaced towards the high wing i too small ii displaced towards the low wing i too large ii displaced towards the low wing
 (i) too small, (ii) displaced towards the high wing.
(i) too small, (ii) displaced towards the high wing. The most forward cg location may be limited by .1 insufficient flare capability ?
Question 230-4 : 1 3 2 3 1 2
 1, 3.
1, 3. Which statement concerning longitudinal stability and control is correct ?
Question 230-5 : A bob weight and a down spring have the same effect on the stick force stability a down spring only improves the manoeuvre stability a down spring has the same function as a stick pusher a bob weight reduces the stick force per g
 A bob-weight and a down-spring have the same effect on the stick force stability.
A bob-weight and a down-spring have the same effect on the stick force stability. When a turn is initiated adverse yaw is ?
Question 230-6 : The tendency of an aeroplane to yaw in the opposite direction of turn mainly due to the difference in induced drag on each wing a momentary yawing motion opposite to the turn due to an incorrect differential aileron movement the tendency of an aeroplane to yaw in the opposite direction of turn mainly due to the difference in aileron form drag the tendency of an aeroplane to yaw in the same direction of turn due to the different wing speeds
 The tendency of an aeroplane to yaw in the opposite direction of turn mainly due to the difference in induced drag on each wing.
The tendency of an aeroplane to yaw in the opposite direction of turn mainly due to the difference in induced drag on each wing. During the take off roll when the pilot raises the tail in a tail wheeled ?
Question 230-7 : Gyroscopic precession asymmetric blade effect torque reaction slipstream
 Gyroscopic precession.
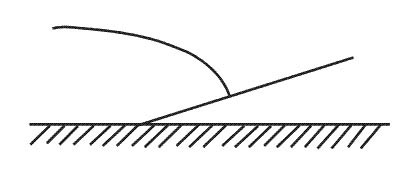
Gyroscopic precession. Assuming no pilot input the motion of the aeroplane in the diagram shows . err ?
Question 230-8 : Dynamic longitudinal stability dynamic longitudinal instability neutral dynamic longitudinal stability static longitudinal instability
 Dynamic longitudinal stability.
Dynamic longitudinal stability. Assuming no pilot input the motion of the aeroplane in the diagram shows . err ?
Question 230-9 : Neutral dynamic longitudinal stability dynamic longitudinal instability dynamic longitudinal stability static longitudinal instability
 Neutral dynamic longitudinal stability.
Neutral dynamic longitudinal stability. Which of the following statements is correct .i a high limit load factor ?
Question 230-10 : I is correct and ii is incorrect i is correct and ii is correct i is incorrect and ii is incorrect i is incorrect and ii is correct
 I is correct and ii is incorrect.
I is correct and ii is incorrect. What is the recommended action following failure of the yaw damper s of a jet ?
Question 230-11 : Reduce altitude and mach number no action is required increase mach number to improve aerodynamic damping of any subsequent dutch roll motion manually recover any subsequent dutch roll motion using rudder
 Reduce altitude and mach number.
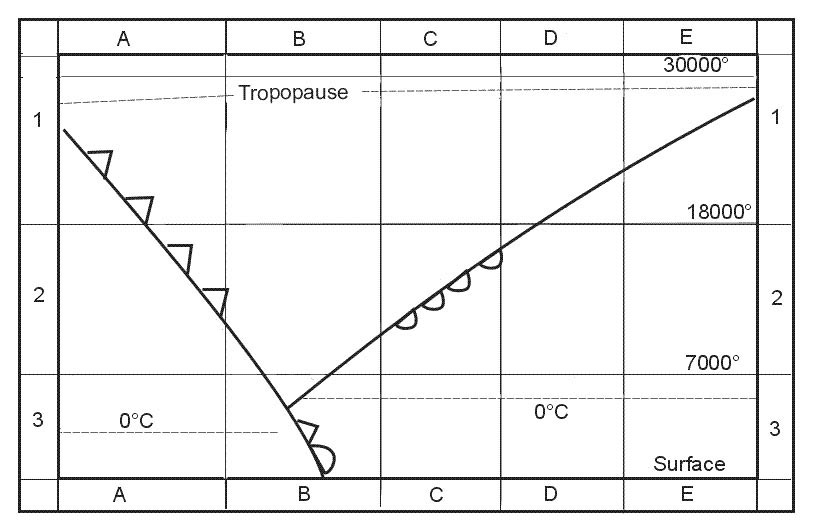
Reduce altitude and mach number. Where on the curve in the diagram does the aeroplane exhibit neutral static ?
Question 230-12 : Point 2 part 1 part 3 the whole curve
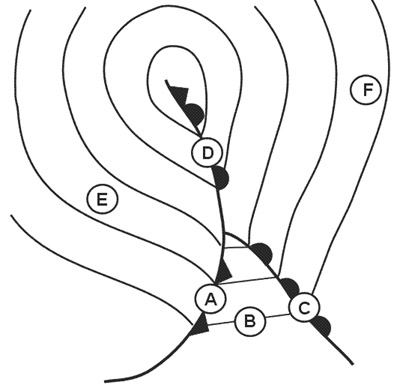 Point 2.
Point 2. Excessive static lateral stability is an undesirable characteristic for a ?
Question 230-13 : It would impose excessive demands on roll control during a sideslip performing co ordinated turns would be very difficult it would result in a proportional decline in static directional stability it would result in excessive wing loading during a co ordinated turn
 It would impose excessive demands on roll control during a sideslip.
It would impose excessive demands on roll control during a sideslip. Where on the curve in the diagram does the aeroplane exhibit static ?
Question 230-14 : Part 1 point 2 part 3 the whole curve
 Part 1.
Part 1. Where on the curve in the diagram does the aeroplane exhibit static ?
Question 230-15 : Part 3 point 2 part 1 the whole curve
 Part 3.
Part 3. Static lateral stability will be increased by ?
Question 230-16 : Increasing wing sweepback reducing the size of the vertical tail the use of a low rather than high wing mounting increasing wing anhedral
 Increasing wing sweepback.
Increasing wing sweepback. Static lateral stability will be increased by ?
Question 230-17 : The use of a high rather than low wing mounting reducing the size of the vertical tail increasing wing anhedral reducing wing sweepback
 The use of a high, rather than low, wing mounting.
The use of a high, rather than low, wing mounting. Turning motion in a steady level co ordinated turn is created by ?
Question 230-18 : The centripetal force the centrifugal force the thrust the drag
 The centripetal force.
The centripetal force. During a short period oscillation the altitude ?
Question 230-19 : Remains approximately constant whereas during a phugoid it varies significantly remains approximately constant as it does during a phugoid varies significantly as it does during a phugoid varies significantly whereas during a phugoid it remains approximately constant
 Remains approximately constant, whereas during a phugoid it varies significantly.
Remains approximately constant, whereas during a phugoid it varies significantly. The purpose of a dorsal fin is to ?
Question 230-20 : Maintain static directional stability at large sideslip angles stabilise forebody vortices reduce tendency for spiral instability provide pitch and yaw control
 Maintain static directional stability at large sideslip angles.
Maintain static directional stability at large sideslip angles. Assuming no pilot input the motion of the aeroplane in the diagram shows . err ?
Question 230-21 : Static longitudinal stability and dynamic longitudinal instability static and dynamic longitudinal stability neutral dynamic longitudinal stability static longitudinal instability
 Static longitudinal stability and dynamic longitudinal instability.
Static longitudinal stability and dynamic longitudinal instability. The centre of gravity moving aft will ?
Question 230-22 : Increase the elevator up effectiveness decrease the elevator up effectiveness not affect the elevator up or down effectiveness increase or decrease the elevator up effectiveness depending on wing location
 Increase the elevator up effectiveness.
Increase the elevator up effectiveness. When the cg position is moved forward the elevator deflection for a manoeuvre ?
Question 230-23 : Larger smaller unchanged dependent on trim position
 Larger.
Larger. Which of the following statements about a mach trimmer is correct ?
Question 230-24 : A mach trimmer corrects the change in stick force stability of a swept wing aeroplane above a certain mach number a straight wing aeroplane always needs a mach trimmer for flying at mach numbers close to mmo a mach trimmer reduces the stick force stability of a straight wing aeroplane to zero at high mach numbers the mach trimmer corrects the natural tendency of a swept wing aeroplane to pitch up
 A mach trimmer corrects the change in stick force stability of a swept wing aeroplane above a certain mach number.
A mach trimmer corrects the change in stick force stability of a swept wing aeroplane above a certain mach number. During initiation of a turn with speedbrakes extended the roll spoiler function ?
Question 230-25 : Downward on the upgoing wing and upward on the downgoing wing upward on the upgoing wing and downward on the downgoing wing on the upgoing wing only on the downgoing wing only
 Downward on the upgoing wing and upward on the downgoing wing.
Downward on the upgoing wing and upward on the downgoing wing. Stick forces provided by an elevator feel system depend on ?
Question 230-26 : Elevator deflection dynamic pressure stabiliser position static pressure elevator deflection static pressure stabiliser position total pressure
 Elevator deflection, dynamic pressure.
Elevator deflection, dynamic pressure. Differential aileron deflection ?
Question 230-27 : Equals the drag of the right and left aileron is required to keep the total lift constant when ailerons are deflected increases the clmax is required to achieve the required roll rate
 Equals the drag of the right and left aileron.
Equals the drag of the right and left aileron. Which kind of 'tab' is commonly used in case of manual reversion of fully ?
Question 230-28 : Servo tab spring tab balance tab anti balance tab
 Servo tab.
Servo tab. One advantage of a movable stabiliser system compared with an elevator trim ?
Question 230-29 : It is a more effective means of trimming the complete system structure and control mechanism weighs less it leads to greater stability in flight the system's complexity is reduced
 It is a more effective means of trimming.
It is a more effective means of trimming. Which statement is correct about a spring tab ?
Question 230-30 : At high ias it behaves like a servo tab at low ias it behaves like a servo tab at high ias it behaves like a fixed extension of the elevator its main purpose is to increase stick force per g
 At high ias it behaves like a servo tab.
At high ias it behaves like a servo tab. How is adverse yaw compensated for during entry into and roll out from a turn ?
Question 230-31 : Differential aileron deflection horn balanced controls anti balanced rudder control servo tabs
 Differential aileron deflection.
Differential aileron deflection. One method to compensate adverse yaw is ?
Question 230-32 : A differential aileron a balance tab an anti balance tab a balance panel
 A differential aileron.
A differential aileron. Flaperons are controls which combine the function of ?
Question 230-33 : Ailerons and flaps ailerons and elevator flaps and speed brakes flaps and elevator
 Ailerons and flaps.
Ailerons and flaps. In general transport aeroplanes with power assisted flight controls are fitted ?
Question 230-34 : Effectiveness of trim tabs is insufficient for those aeroplanes the pilot does not feel the stick forces at all mechanical adjustment of trim tabs creates too many problems trim tab deflection increases vmo
 Effectiveness of trim tabs is insufficient for those aeroplanes.
Effectiveness of trim tabs is insufficient for those aeroplanes. A jet aeroplane equipped with inboard and outboard ailerons is cruising at its ?
Question 230-35 : Only the inboard ailerons are active only the outboard aileron are active the inboard and outboard ailerons are active only the spoilers will be active not the ailerons
 Only the inboard ailerons are active.
Only the inboard ailerons are active. Which of the following statements concerning control is correct ?
Question 230-36 : In a differential aileron control system the control surfaces have a larger upward than downward maximum deflection on some aeroplanes the servo tab also serves as a trim tab hydraulically powered control surfaces do not need mass balancing in general the maximum downward elevator deflection is larger than upward
When are outboard ailerons if present de activated ?
Question 230-37 : Flaps and slats retracted or speed above a certain value flaps and/or slats extended or speed below a certain value landing gear retracted landing gear extended
 Flaps (and slats) retracted or speed above a certain value.
Flaps (and slats) retracted or speed above a certain value. Which statement about stick force per g is correct ?
Question 230-38 : The stick force per g must have both an upper and lower limit in order to ensure acceptable control characteristics the stick force per g increases when centre of gravity is moved aft the stick force per g can only be corrected by means of electronic devices stability augmentation in case of an unacceptable value if the slope of the fe n line becomes negative generally speaking this is not a problem for control of an aeroplane
 The stick force per g must have both an upper and lower limit in order to ensure acceptable control characteristics.
The stick force per g must have both an upper and lower limit in order to ensure acceptable control characteristics. Examples of aerodynamic balancing of control surfaces are ?
Question 230-39 : Servo tab spring tab seal between the wing trailing edge and the leading edge of control surface balance tab horn balance and mass balance mass in the nose of the control surface horn balance and mass balance spring tab servo tab and power assisted control
 Servo tab, spring tab, seal between the wing trailing edge and the leading edge of control surface.
Servo tab, spring tab, seal between the wing trailing edge and the leading edge of control surface. Which phenomenon is counteracted with differential aileron deflection ?
Question 230-40 : Adverse yaw aileron reversal sensitivity for spiral dive turn co ordination
 Adverse yaw.
Adverse yaw. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
9159 Free Training Exam
