Which 'code letter' shall be chosen to identify a taxiway to be used by an ? [ Control visibility ]
Question 24-1 : Code letter 'c' code letter 'e' code letter 'd' code letter 'b'
 Code letter 'c'.
Code letter 'c'. Which of the following alternatives describes the complete cat 1 'calvert' type ?
Question 24-2 : 5 crossbars centre line with 3 2 and 1 lamp per light unit 4 crossbars centre line with 3 or 2 lamps per light unit 3 crossbars centre line with 3 2 or 1 lamp per light unit 3 crossbars centre line with 3 or 2 lamps per light unit
 5 crossbars, centre line with 3, 2 and 1 lamp per light unit.
5 crossbars, centre line with 3, 2 and 1 lamp per light unit. Within the annex to the icao convention that specifies dimensions of aerodromes ?
Question 24-3 : 45 metres 35 metres 40 metres 50 metres
 45 metres.
45 metres. White or yellow crosses painted or located at the thresholds and on the runway ?
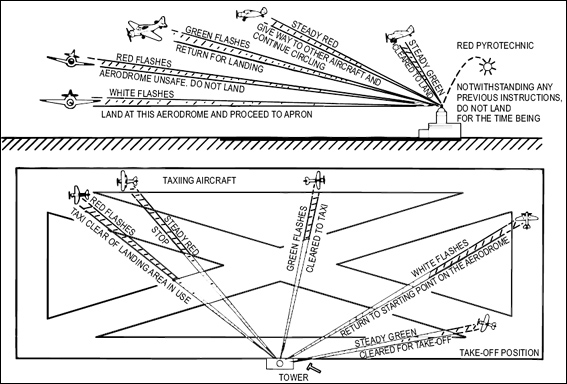
Question 24-4 : This runway is closed landing is prohibited aircraft are required to land and take off on this runway and all other manoeuvres need to be confined to taxiways this runway is being used by gliders and that glider flights are being performed special precautions must be observed due to bad state of this runway
 This runway is closed, landing is prohibited.
This runway is closed, landing is prohibited. Mandatory instructions signs on an aerodrome shall have the following colours ?
Question 24-5 : White inscription on a red background black inscriptions on a red background yellow inscriptions on a black background black inscriptions on a yellow background
 White inscription on a red background.
White inscription on a red background. A runway strip is ?
Question 24-6 : An area intended to reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off a runway a taxiway strip a clearway a defined area where aircraft can be held or bypassed to facilitate efficient surface movement
 An area intended to reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off a runway.
An area intended to reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off a runway. What is the name for a taxiway connected to a runway at an acute angle designed ?
Question 24-7 : Rapid exit taxiway rapid turn off lane high speed exit lane acute angle exit
 Rapid exit taxiway.
Rapid exit taxiway. Radio altimeter operating area.a radio altimeter operating area shall extend ?
Question 24-8 : 300 m 450 m 500 m 100 m
 300 m.
300 m. Approach lighting systems .the length of a simple approach lighting system ?
Question 24-9 : 420 m 300 m 150 m 600 m
 420 m.
420 m. The colour of a runway designation marking on a paved runway shall be ?
Question 24-10 : White blue red yellow
 White.
White. Annex 14 to the convention on international civil aviation contains standards ?
Question 24-11 : Aerodromes security search and rescue facilitation
 Aerodromes.
Aerodromes. A detailed description of the visual ground aids can be found in icao ?
Question 24-12 : Annex 14 annex 3 annex 13 annex 17
 Annex 14.
Annex 14. Annex 14 rescue and fire fighting.the most important factors bearing on ?
Question 24-13 : The training received the effectiveness of the equipment and the speed with which personnel and equipment designated for rescue and fire fighting purposes can be put into use the size of the aircraft and the number of fire extinguishers on board the aircraft the effectiveness of the equipments the time of the day the weather the speed of the impact and the location of the impact
 The training received, the effectiveness of the equipment and the speed with which personnel and equipment designated for rescue and fire fighting purposes can be put into use.
The training received, the effectiveness of the equipment and the speed with which personnel and equipment designated for rescue and fire fighting purposes can be put into use. Annex 14 rescue and fire fighting.the principal objective of a rescue and ?
Question 24-14 : To save lives to avoid accidents to provide efficient training to the flight crew to extinguish fires
 To save lives.
To save lives. Annex 14 rescue and fire fighting.what is meant by the term 'response time' ?
Question 24-15 : Between the initial call to the rff service and the time when the first responding vehicle s is are in position to apply foam between the initial call to the rff service and the time when the first responding vehicle s is are leaving the fire station between the first responding vehicle leaving the fire station and the time to secure the impact area taken by the first responding vehicle to reach the impact area
Annex 14 rescue and fire fighting.the operational objective of the rescue and ?
Question 24-16 : Two minutes and not exceeding three minutes to the end of each runway as well as to any other part of the movement area in optimum conditions of visibility and surface conditions three minutes and not exceeding four minutes to the end of each runway as well as to any other part of the movement area in optimum conditions of visibility and surface conditions five minutes to the end of each runway as well as to any other part of the movement area in optimum conditions of visibility and surface conditions two minutes to the end of each runway as well as to any other part of the movement area in optimum conditions of visibility and surface conditions
 Two minutes and not exceeding three minutes to the end of each runway, as well as to any other part of the movement area, in optimum conditions of visibility and surface conditions.
Two minutes and not exceeding three minutes to the end of each runway, as well as to any other part of the movement area, in optimum conditions of visibility and surface conditions. A no entry signal has to be established as follows ?
Question 24-17 : On both sides at the beginning of the affected zone on the right side of the taxiway on the left side of the taxiway on the right side of the taxiway 50 m before the affected zone
Annex 14 aerodromes .the height of signs near a runway or taxiway shall be ?
Question 24-18 : Preserve clearance for propellers and the engine pods of jet aircraft provide best visibility for pilots preserve clearance for wings prevent damage to aircraft or vehicles
 Preserve clearance for propellers and the engine pods of jet aircraft.
Preserve clearance for propellers and the engine pods of jet aircraft. Annex 14 aerodromes .the height of markers and elevated lights near a runway ?
Question 24-19 : Preserve clearance for propellers and the engine pods of jet aircraft provide best visibility for pilots prevent damage to aircraft or vehicles preserve clearance for wings
 Preserve clearance for propellers and the engine pods of jet aircraft.
Preserve clearance for propellers and the engine pods of jet aircraft. If more than 25% of a runway is covered by 3mm of water the runway is ?
Question 24-20 : Contaminated wet damp flooded
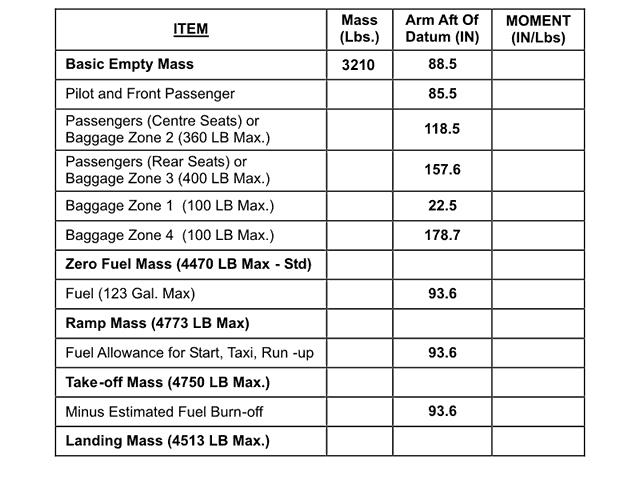 Contaminated.
Contaminated. Declared distances .tora take off run available is ?
Question 24-21 : The length of runway declared available and suitable for the ground run of an aeroplane taking off the length of the take off run available plus the length of the clearway if provided the length of the take off run available plus the length of stop way if provided the length of the take off run available plus the length of the stop way and clearway if provided
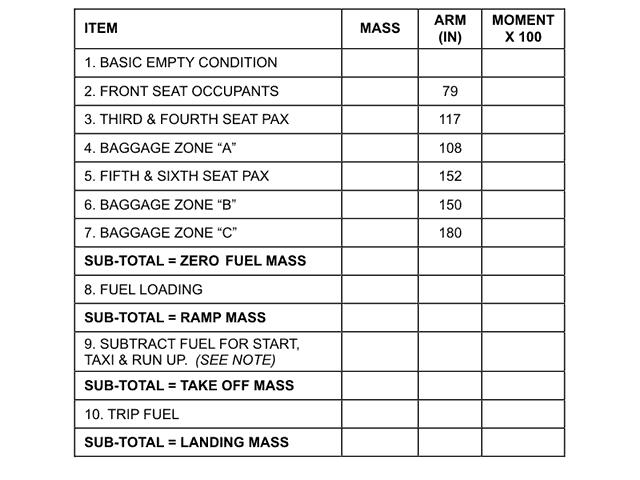 The length of runway declared available and suitable for the ground run of an aeroplane taking-off.
The length of runway declared available and suitable for the ground run of an aeroplane taking-off. The four declared distances tora toda asda lda are equal to the length of the ?
Question 24-22 : There is no stopway or clearway and no displaced threshold there is no stopway or clearway with a displaced threshold stopway or clearway are equal and no displaced threshold stopway or clearway are equal with a displaced threshold
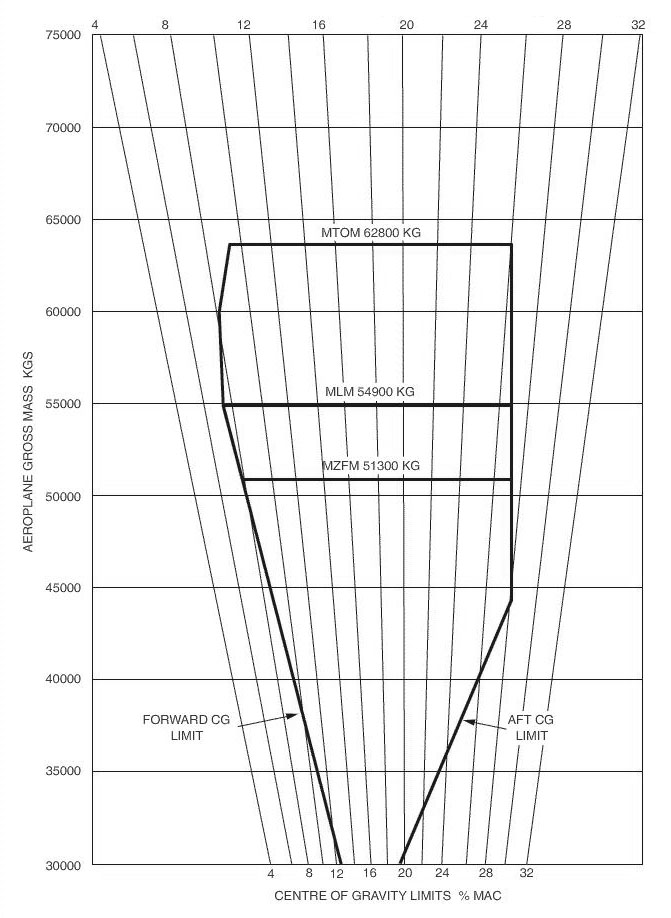 There is no stopway or clearway, and no displaced threshold.
There is no stopway or clearway, and no displaced threshold. Declared distances the four main most important declared runway distances are ?
Question 24-23 : Tora toda asda lda tora toda swy cwy alda tada sdas gbas rway toda cla swy
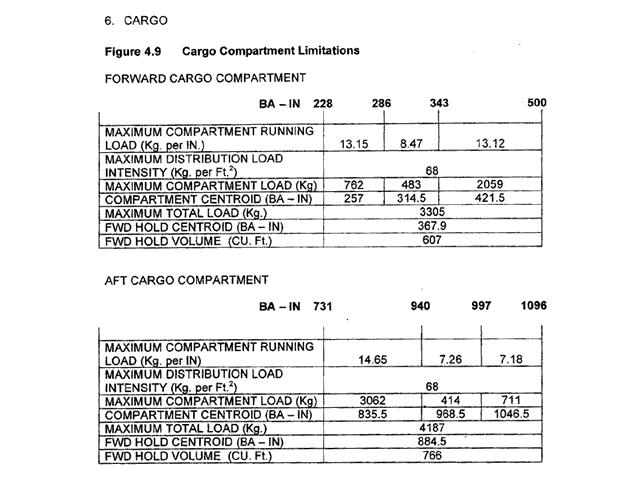 Tora, toda, asda, lda.
Tora, toda, asda, lda. Definitions aerodrome .an area symmetrical about the extended runway centre ?
Question 24-24 : Runway end safety area resa safe land area sla stopway clearway
 Runway end safety area (resa).
Runway end safety area (resa). Definitions aerodrome .a 'runway strip' is a defined area including ?
Question 24-25 : The runway and stopway if provided the runway and clearway if provided the stopway and the runway end safety area resa the clearway
 The runway and stopway if provided.
The runway and stopway if provided. Guidance on calculation of declared distances is given in ?
Question 24-26 : Icao annex 14 attachment a icao annex 10 runway characteristics part 145 ad2 aerodrome data eurocae doc 7000 runway data
 Icao annex 14, attachment a.
Icao annex 14, attachment a. Aerodromes general .abbreviation resa means ?
Question 24-27 : Runway end safety area runway edge safety area runway turn pad area taxiway strip
 Runway end safety area.
Runway end safety area. A resa can be implemented at ?
Question 24-28 : Both ends of the runway strip the end of toda the end of tora runway threshold
 Both ends of the runway strip.
Both ends of the runway strip. Regarding pavement strength the abbreviation acn stands for… ?
Question 24-29 : Aircraft classification number aircraft code number aerodrome code number aerodrome classification number
 Aircraft classification number.
Aircraft classification number. Regarding the bearing strength of aprons runways and taxiways the abbreviation ?
Question 24-30 : Pavement classification number platform code number pavement code number platform classification number
 Pavement classification number.
Pavement classification number. According to icao annex 14 the bearing strength of a pavement intended for ?
Question 24-31 : The maximum allowable aircraft mass and maximum allowable tire pressure a reference category of the aircraft is transmitted the acn/pcn does not refer to aircraft under 5 700 kg the maximum allowable tire pressure category or value and evaluation method
 The maximum allowable aircraft mass and maximum allowable tire pressure.
The maximum allowable aircraft mass and maximum allowable tire pressure. A 'runway strip' is defined as an area including the runway and… ?
Question 24-32 : A stopway if provided intended to reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off a runway and to protect aircraft flying over it during take off and landing operations a taxiway intended to protect an aircraft operating on the runway and to reduce the risk of damage to an aircraft running off the taxiway a clearway if provided intended to reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off a runway and to protect aircraft flying over it a taxiway intended to protect an aircraft operating on the taxiway and to reduce the risk of damage to an aircraft running off the runway
 A stopway, if provided, intended to reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off a runway and to protect aircraft flying over it during take-off and landing operations.
A stopway, if provided, intended to reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off a runway and to protect aircraft flying over it during take-off and landing operations. Icao annex 14 the runway strip ?
Question 24-33 : Includes the runway and if provided the stopway has the same length as the runway is located at the end of the runway end safety area defines the dimensions of the ils critical area
 Includes the runway and, if provided, the stopway.
Includes the runway and, if provided, the stopway. One of the purposes of the runway strip is to… ?
Question 24-34 : Reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off the runway define the distance from the runway centre line to the holding point protect other aircraft during engine run up tests prevent wildlife from entering the runway
 Reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off the runway.
Reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off the runway. What does resa mean ?
Question 24-35 : Runway end safety area runway excursion safety area runway end security area runway enhanced safety area
 Runway end safety area
Runway end safety area What is the icao definition for clearway ?
Question 24-36 : A defined rectangular area on the ground or water selected or prepared as a suitable area over which an aircraft may make a portion of its initial climb to a specified height a defined rectangular area on the ground at the end of take off run available prepared as a suitable area in which an aircraft can be stopped in the case of an abandoned take off a defined area including the runway and stopway intended to protect aircraft flying over it during take off or landing operations an area symmetrical about the extended runway centre line and adjacent to the end of the strip primarily intended to reduce the risk of damage to an aircraft undershooting or overrunning the runway
 A defined rectangular area on the ground or water, selected or prepared as a suitable area over which an aircraft may make a portion of its initial climb to a specified height.
A defined rectangular area on the ground or water, selected or prepared as a suitable area over which an aircraft may make a portion of its initial climb to a specified height. If a clearway is provided its length is part of the… ?
Question 24-37 : Take off distance available toda accelerate stop distance available asda landing distance available lda take off runway available tora
 Take-off distance available (toda).
Take-off distance available (toda). How wide must a stopway be ?
Question 24-38 : As wide as the associated runway as wide as the associated runway strip as wide as the obstacle free zone half as wide as the associated runway
 As wide as the associated runway.
As wide as the associated runway. The stopway is located at the end of the ?
Question 24-39 : Take off run available tora accelerate stop distance available asda landing distance available lda take off distance available toda
 Take-off run available (tora).
Take-off run available (tora). What is the icao definition for stopway ?
Question 24-40 : A defined rectangular area on the ground at the end of take off run available prepared as a suitable area in which an aircraft can be stopped in the case of an abandoned take off a defined rectangular area on the ground at the end of take off run available prepared to reduce the risk of damage to aircraft running off a runway a defined rectangular area on the ground or water established to protect aircraft during take off or landing operations a defined rectangular area on the ground or water established to permit aircraft to make a portion of its initial climb to a specific height
 A defined rectangular area on the ground at the end of take-off run available prepared as a suitable area in which an aircraft can be stopped in the case of an abandoned take-off.
A defined rectangular area on the ground at the end of take-off run available prepared as a suitable area in which an aircraft can be stopped in the case of an abandoned take-off. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
919 Free Training Exam Other source study: Furious atpl examen 24
